Search the whole station Crushing Equipment
The single cylinder rotary dryer is for drying bulk materials in various industries: building materials, metallurgical, chemical, glass, etc. On the basis of heat engineering calculations, we select the most optimal dryer size and design for customer requirements.
The capacity of the drum dryer is from 0.5 tph to 100 tph. According to the calculations, a loading chamber, a burner, an unloading chamber, a mechanism for dust collecting and gas cleaning are manufactured. The dryer adopts automation system and a frequency drive to adjust the temperature and rotation speed. This makes it possible to vary the drying parameters and overall performance within a wide range.
You need a rotary dryer for one primary reason: control. Raw materials from a quarry or stockpile have inconsistent moisture levels. This inconsistency is a disaster for any precise manufacturing process, like making concrete blocks. If your sand is too wet, your blocks will slump and have low strength. If it is too dry, it can absorb too much water from the mix, starving the cement of the water it needs for proper hydration. A drying system removes this variable. It gives you a perfectly consistent raw material, which directly leads to:
Ultimately, a rotary dryer gives you control over your process, and control is the key to profit.
Rotary dryers are mainly categorized by how they heat the material. The two most common types are direct heat and indirect heat dryers. Understanding the difference is crucial for choosing the right machine.
The what is a rotary dryer used for question has countless answers, as its applications span dozens of industries. At ZONEDING, we focus on heavy industrial applications where reliability is key. Some of the most common uses include:
Rotary dryer is suitable to dry metallic and non-metallic mineral, clay in cement industry and coal in coal mine etc. For example, sand, vinasse, slag ,sludge, coal powder, sawdust, limestone powder, rice husk, mineral powder , clay, etc.
A rotary dryer is incredibly versatile. It can handle a huge range of materials, provided they are in a bulk or granular form. Here is a short list of common materials:








Very sticky materials may require a back-mixing system to prevent them from clumping and sticking to the dryer shell.
The working principle of a rotary dryer is based on gravity and heat exchange.
The wet materials that need to be dried are sent to the feeding hopper by a belt conveyor or a hoist, and then enter the material end through the feeding pipe. The slope of the feeding tube is greater than the natural inclination of the material, so that the material can enter the dryer smoothly.
The dryer cylinder is a rotating cylinder slightly inclined from the horizontal line. The material is added from the higher end, and the heating medium is in contact with the material. With the rotation of the cylinder, the material moves to the lower end under the action of gravity. In the process, the material and the heat carrier exchange heat directly or indirectly, so that the material is dried, and then sent out through a belt conveyor or a screw conveyor.
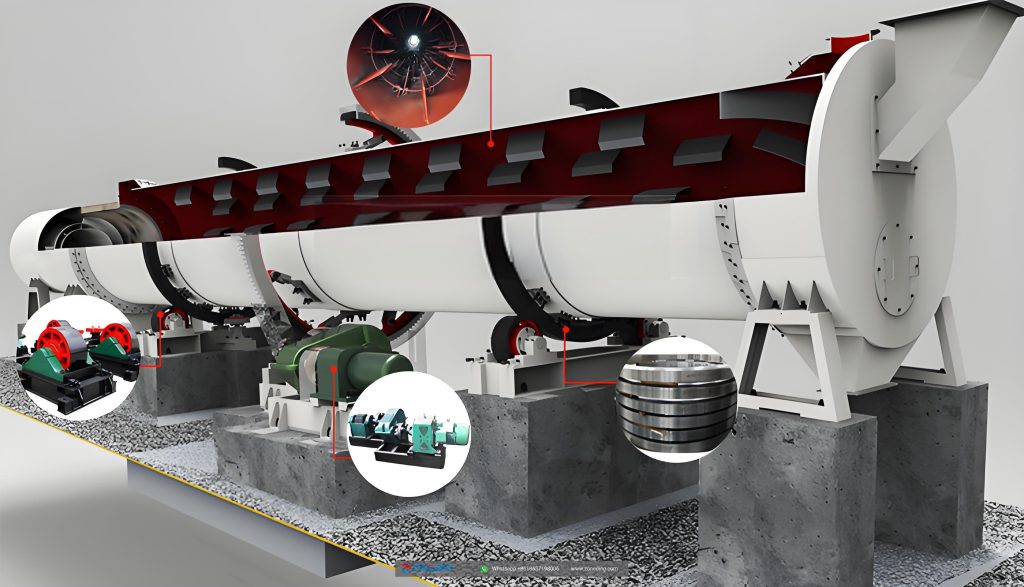
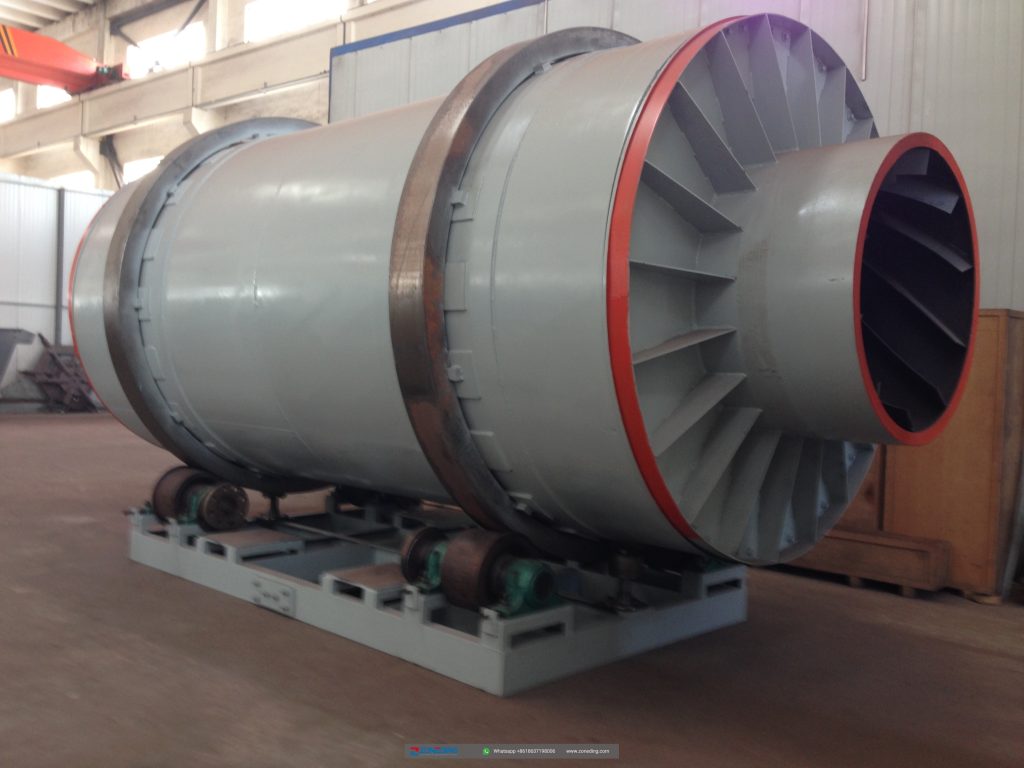
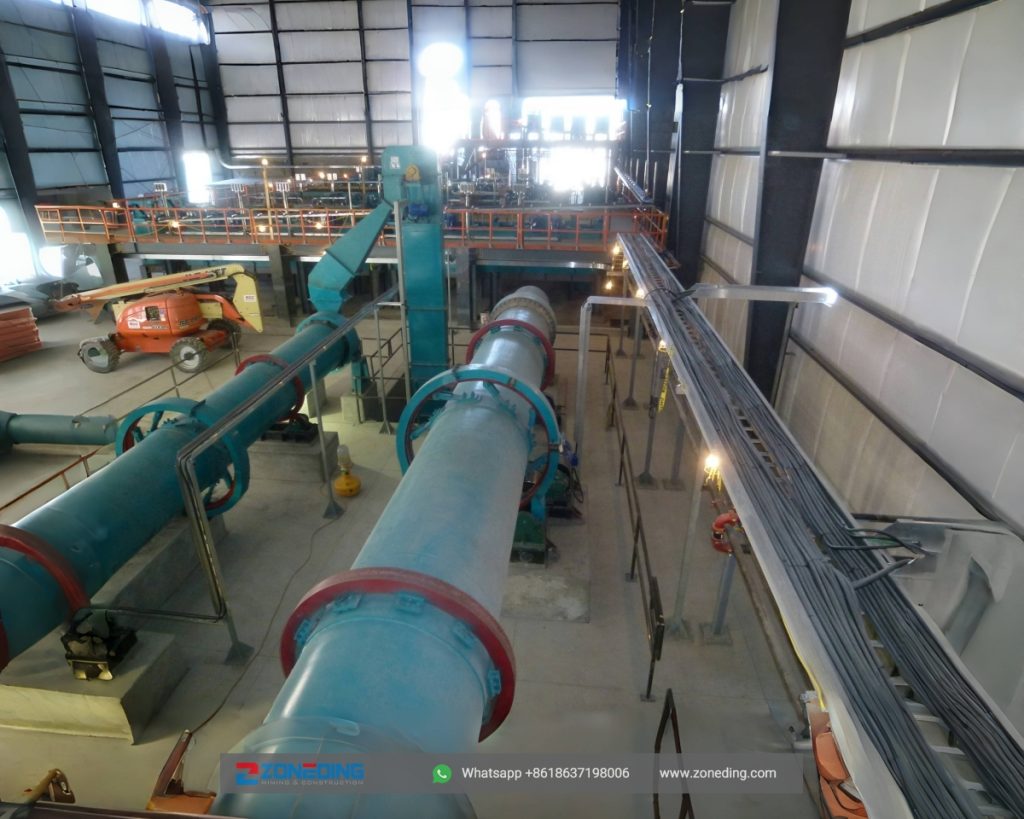
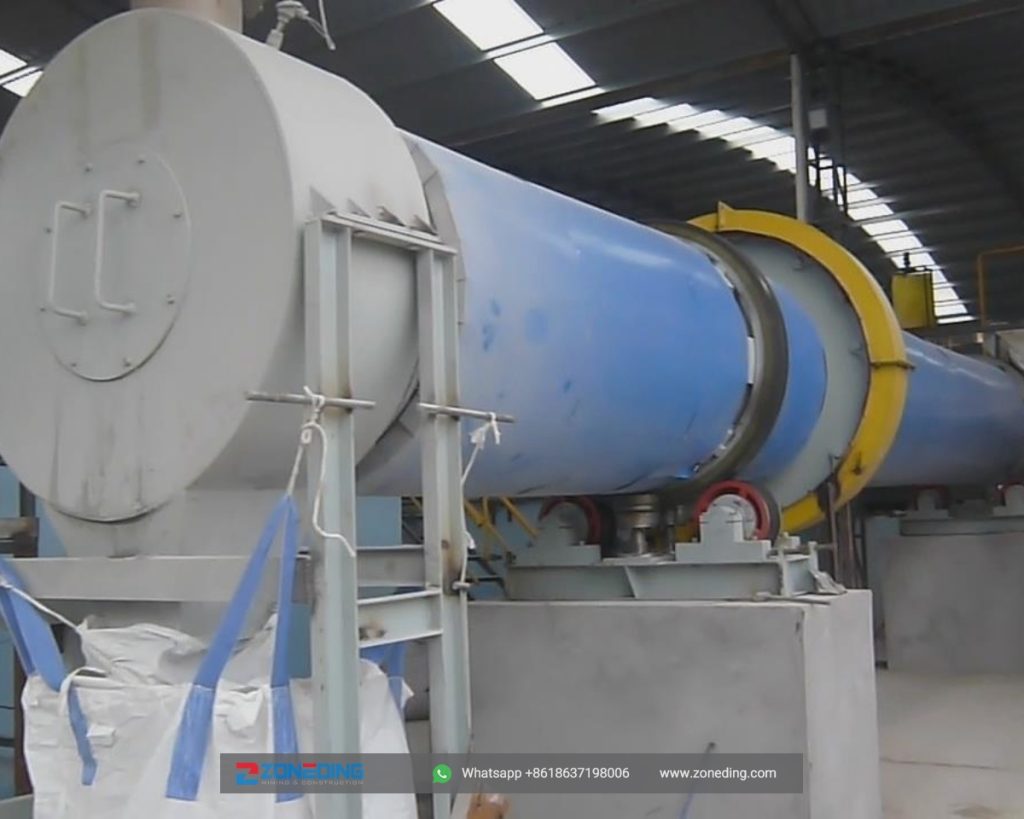
When you look at a rotary dryer, it might seem like a simple steel tube. However, the difference between a machine that lasts 5 years and one that lasts 30 years is in the engineering details. At ZONEDING, we build our dryers for long-term performance and reliability. A critical feature to examine is the trunnion rings (tires) and the girth gear. A cheap dryer might use a simple rolled steel bar for its tires, which wears unevenly and can’t be repaired. We use forged and machined trunnion rings. They are perfectly round, have hardened surfaces, and are designed to be resurfaced in-place after decades of service.
Similarly, the girth gear that turns the drum must be a two-piece or four-piece, cast steel, spring-mounted design. A one-piece gear welded to the shell cannot absorb the immense stress from thermal expansion and flexing. This stress will eventually crack the gear or the shell itself. Our spring-mounted design allows the gear to “float,” isolating it from these forces and ensuring a multi-decade lifespan. These are not just features; they are a philosophy of building equipment that becomes a long-term asset, not a short-term expense.
Gas burners, light oil burners, heavy oilburners, pulverized coal burners, andbiomass pellet burner, etc.
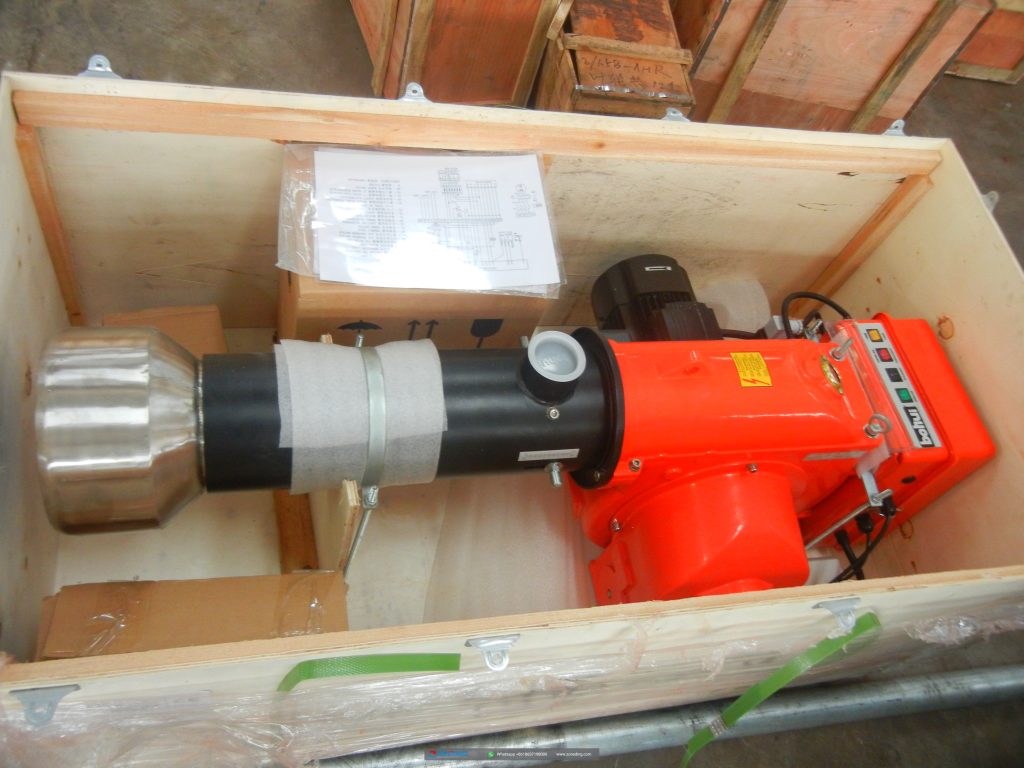
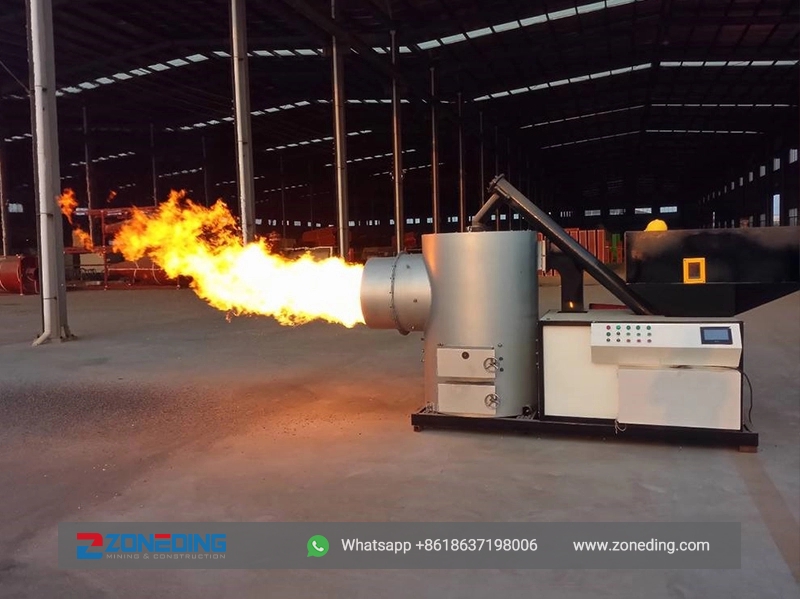



Provide space for fuel combustion, theend of the chamber is provided with anair inlet and an air regulating valve, andthe interior is built with refractory
cement and bricks, and the temperaturein the burning chamber can reach up to1200 C. lts structure is exquisite andreasonable, and it is closely combinedwith the dryer cylinder to providesufficient heat source for the dryer
Given different structures and applications, the rotary drum dryer is divided into several types. And thus, drying technology is more targeted.
According to the structure, rotary dryers are divided into the single-cylinder type and multi-cylinder type.
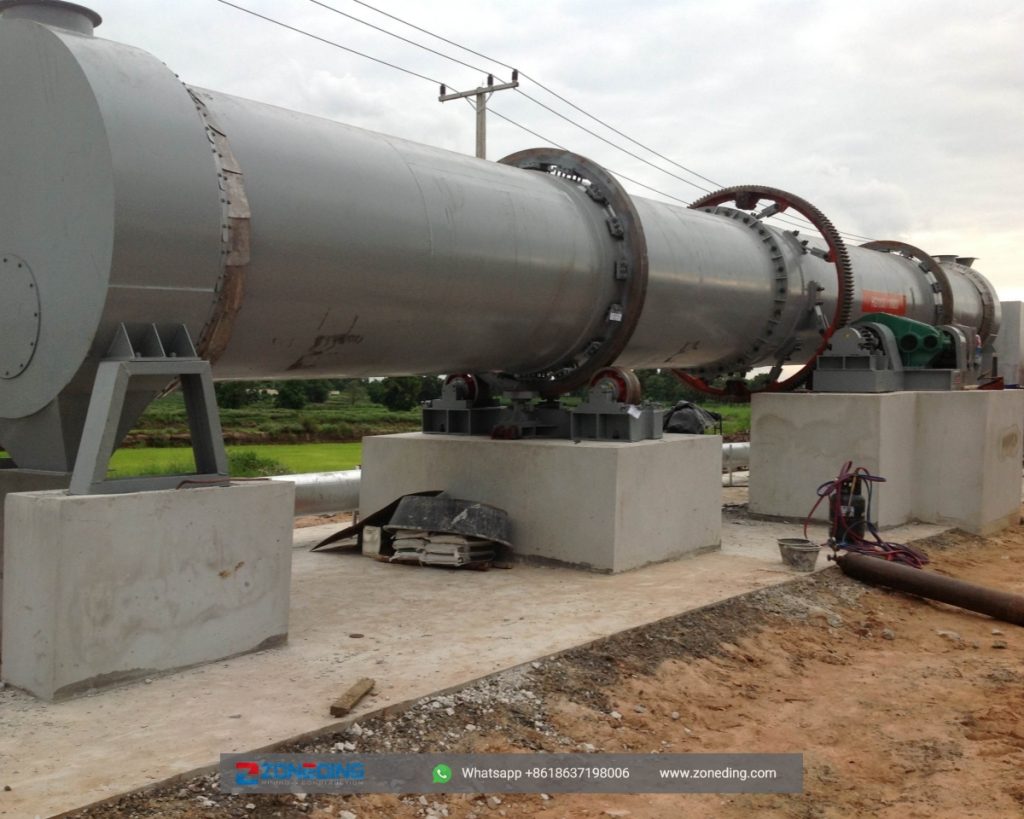
Based on experience and customer feedback, Zoneding engineers will recommend the single-cylinder rotary dryer. These two types of rotary dryers have almost the same drying efficiency. While the structure of the single-cylinder one is simpler, resulting in more convenient daily maintenance. The maintenance personnel can directly get into the cylinder body for inspection. For multi-cylinder dryers, this is difficult to achieve.
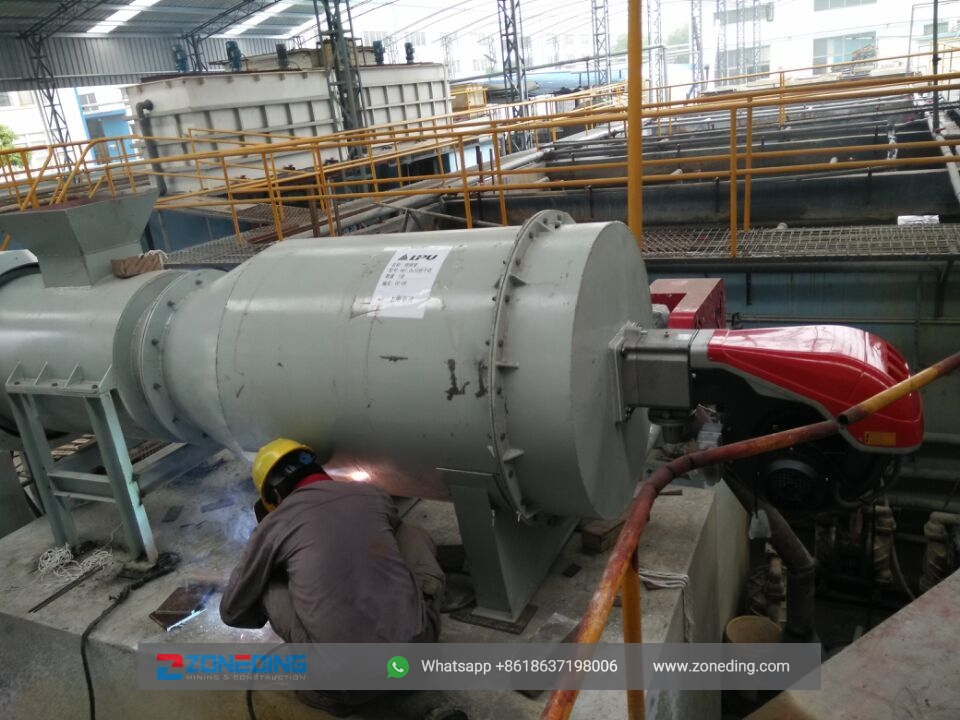
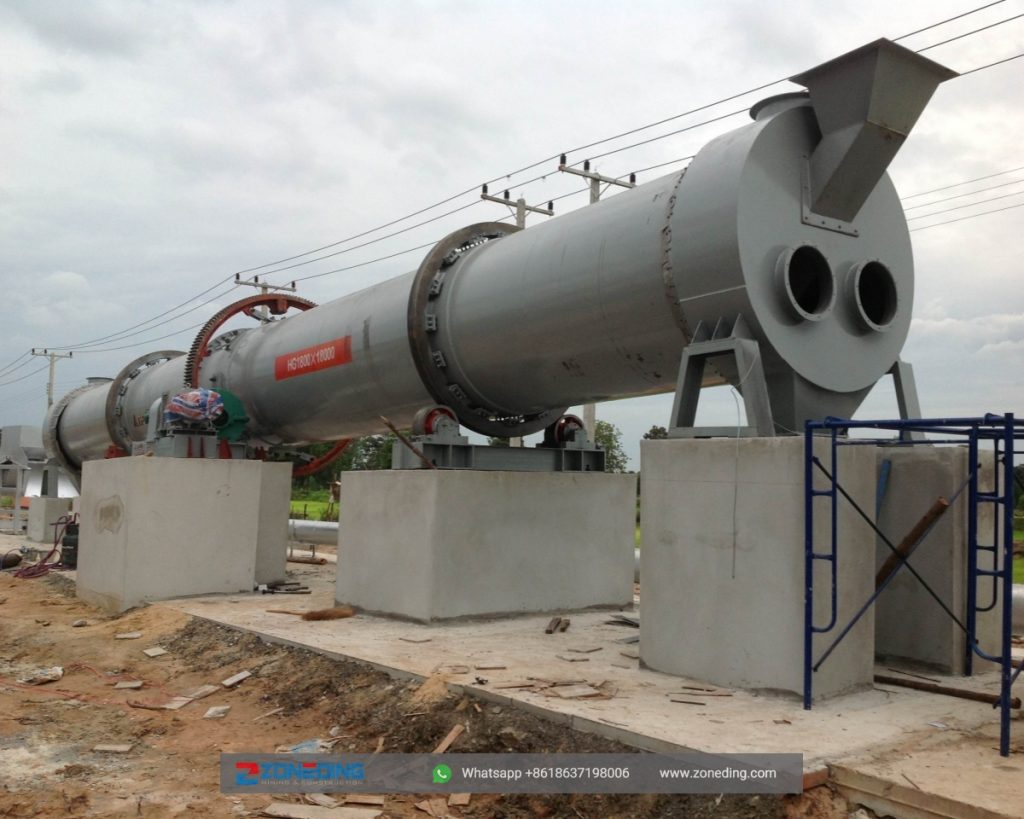
Working site of single-cylinder rotary dryer and multi-cylinder rotary dryer
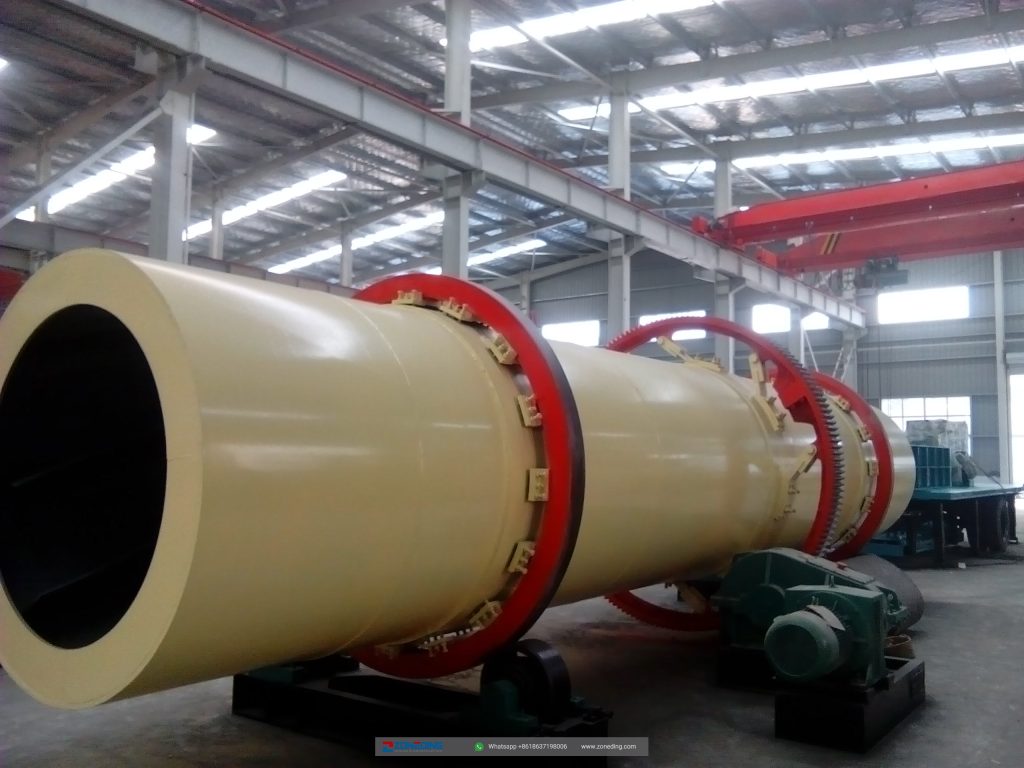


According to the heat transfer mode, the rotary dryer is divided into the direct type and indirect type, or it can also be divided into a co-current rotary dryer and counter-current rotary dryer.
The main structure of a rotary drum dryer consists of several key parts working together:
The rotary dryer working principle is a combination of mechanics and thermodynamics. Material is fed into the high end of the tilted, rotating drum. Inside the drum are a series of metal plates called “lifters.” As the drum rotates, these lifters pick up the material and drop it from the top of the drum down to the bottom. This process is repeated over and over as the material slowly moves down the length of the dryer. The most important part of this process is the creation of a “curtain.”
Efficiency is not about maximum temperature; it is about the curtain. The most efficient heat transfer happens when the lifters distribute the material in a uniform, dense curtain that fills the entire cross-section of the drum. Hot gas from the burner is forced to pass through this curtain, giving up its heat directly to the material. If your lifters are poorly designed or the rotation speed is wrong, you get a poor curtain with big gaps. The hot gas then bypasses the material and goes straight out the smokestack. You could have a 1000°C inlet temperature, but if the gas is not touching the product, you are just heating the sky. A lower temperature with a perfect, dense curtain is vastly more fuel-efficient and is the secret to an effective drying system.
The industrial rotary dryer price can range from $30,000 for a small, simple unit to over $500,000 for a large, high-capacity system. The price depends on one crucial factor: evaporation capacity, not tonnage. This is the single most expensive mistake customers make. They say, “I need a dryer for 20 tons per hour of sand,” and they get a price. But drying 20 tons of sand with 5% starting moisture is completely different from drying 20 tons with 20% starting moisture.
The second scenario requires a machine with four times the evaporation capacity. This means a much larger burner, a larger drum diameter for a longer residence time, and a more powerful fan system. Buying a dryer based on output tonnage without specifying the exact water removal rate is a recipe for failure. You will either buy a machine that is too small and can never meet your goals or one that is oversized and incredibly inefficient. A true price can only be determined after a detailed analysis of your material, moisture content, and production needs.
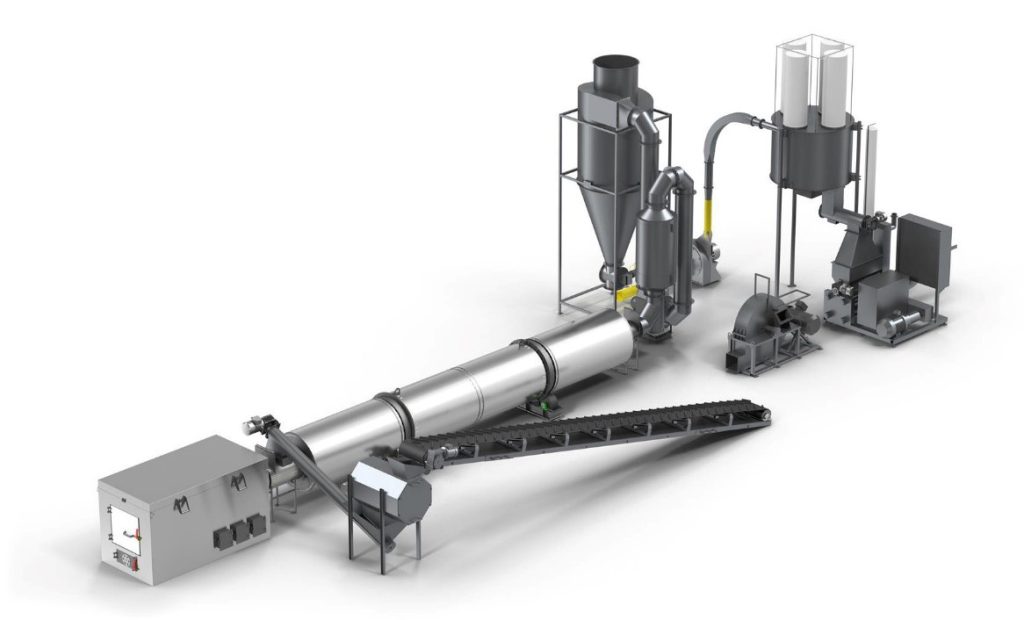
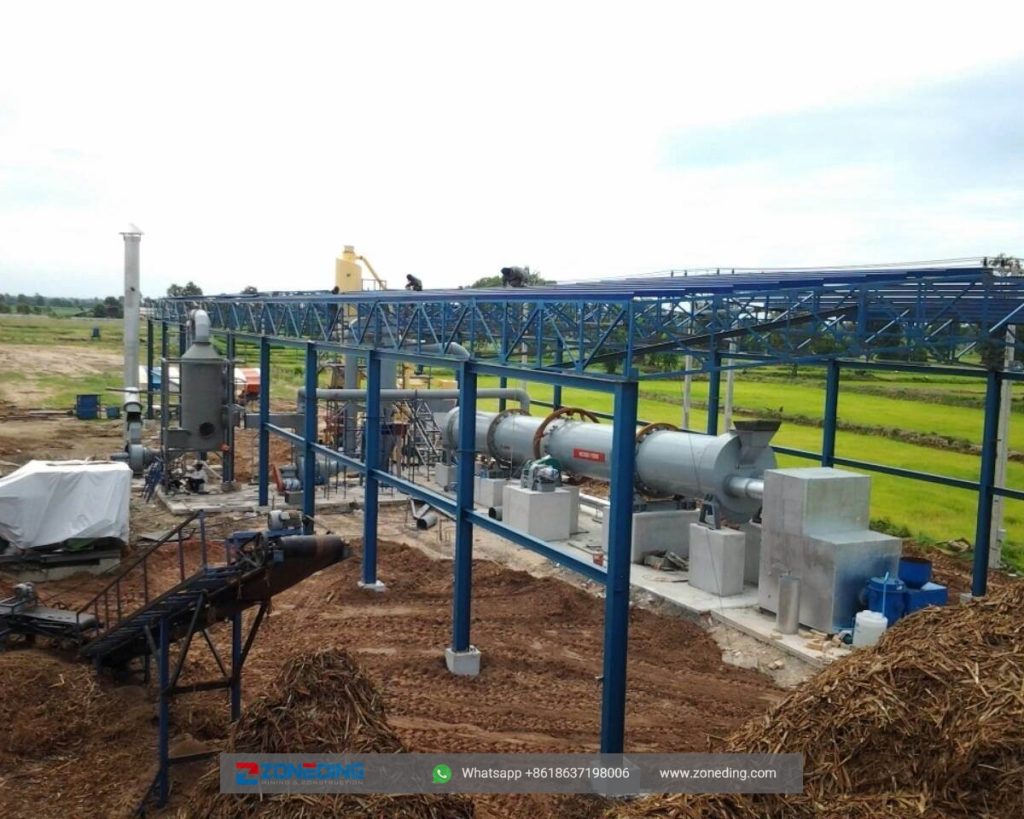
A rotary dryer rarely works alone. It is the central part of a complete drying system. A typical process line includes:
Choosing the right dryer involves a careful engineering review. Here are the key steps we take with our clients:
Proper maintenance is the key to a long and profitable life for your dryer. While regular lubrication and inspections are standard, there is one insider tip we share with all our customers: check the thrust rollers. Your dryer is installed at a slight angle, so the entire multi-ton weight of the drum and material is constantly trying to slide downhill. The thrust rollers are a set of small, powerful wheels that push back against this force, keeping the drum in place.
A properly aligned and lubricated thrust roller should run cool. Once per shift, an operator should safely place their hand near the bearing housing. If it is too hot to keep your hand there, your dryer is misaligned or improperly lubricated. This heat is the first sign of trouble before the roller fails and causes catastrophic damage. This simple, no-cost check is more valuable than any sensor you can buy and can prevent a five-figure repair bill.
At ZONEDING, we are more than just a manufacturer. We are your partners in production. Since 1990, we have specialized in heavy-duty machinery for the building materials industry. When you choose us for your industrial dryer needs, you get:
| Spec./m (Dia.×Length) | Shell Cubage (m³) | Capacity (t/h) | Installation Obliquity(%) | Highest Inlet Air Temperature(℃) | Main Motor (kw) | Weight (t) |
| Φ1.2×8.0 | 9.0 | 1.9~2.4 | 3~5 | 700~800 | 7.5 | 9 |
| Φ1.2×10 | 11.3 | 2.4~3.0 | 3~5 | 700~800 | 7.5 | 11 |
| Φ1.5×12 | 21.2 | 4.5~5.7 | 3~5 | 700~800 | 15 | 18.5 |
| Φ1.5×14 | 24.7 | 5.3~6.6 | 3~5 | 700~800 | 15 | 19.7 |
| Φ1.5×15 | 26.5 | 5.7~7.1 | 3~5 | 700~800 | 15 | 20.5 |
| Φ1.8×12 | 30.5 | 6.5~8.1 | 3~5 | 700~800 | 18.5 | 21.5 |
| Φ1.8×14 | 35.6 | 7.6~9.5 | 3~5 | 700~800 | 18.5 | 23 |
| Φ2.2×12 | 45.6 | 9.7~12.2 | 3~5 | 700~800 | 22 | 33.5 |
| Φ2.2×14 | 53.2 | 11.4~14.2 | 3~5 | 700~800 | 22 | 36 |
| Φ2.2×16 | 60.8 | 13.0~16.2 | 3~5 | 700~800 | 22 | 38 |
| Φ2.4×14 | 63.3 | 13.5~16.9 | 3~5 | 700~800 | 37 | 45 |
| Φ2.4×18 | 81.4 | 17.4~21.7 | 3~5 | 700~800 | 37 | 49 |
| Φ2.4×20 | 90.4 | 19.3~24.1 | 3~5 | 700~800 | 45 | 54 |
| Φ2.4×22 | 99.5 | 21.2~26.5 | 3~5 | 700~800 | 45 | 58 |
| Φ2.6×24 | 127.4 | 27.2~34.0 | 3~5 | 700~800 | 55 | 73 |
| Φ3.0×20 | 141.3 | 30.1~37.7 | 3~5 | 700~800 | 75 | 85 |
| Φ3.0×25 | 176.6 | 37.7~47.1 | 3~5 | 700~800 | 75 | 95 |
| Φ3.2×25 | 201 | 42.9~53.6 | 3~5 | 700~800 | 90 | 110 |
| Φ3.6×28 | 285 | 60.8~76.0 | 3~5 | 700~800 | 160 | 135 |








FAQ
Consistent moisture is the key to consistent product quality. For our block-making clients, under-dried sand causes blocks to slump, while over-dried sand leads to weak, crumbly blocks. Both result in high scrap rates. By delivering sand with a precise and consistent moisture content, a good rotary dryer eliminates this variable, dramatically reducing waste and ensuring every block you make is a sellable, high-quality product.
There are two main ways. First, ensure your dryer has excellent seals to prevent cold air from being sucked in and cooling the system. Second, focus on the “curtain.” Efficient drying happens when the internal lifters create a dense curtain of material for the hot gas to pass through. A well-designed lifter system from a quality manufacturer like ZONEDING ensures maximum heat transfer, getting the most value from every unit of fuel.
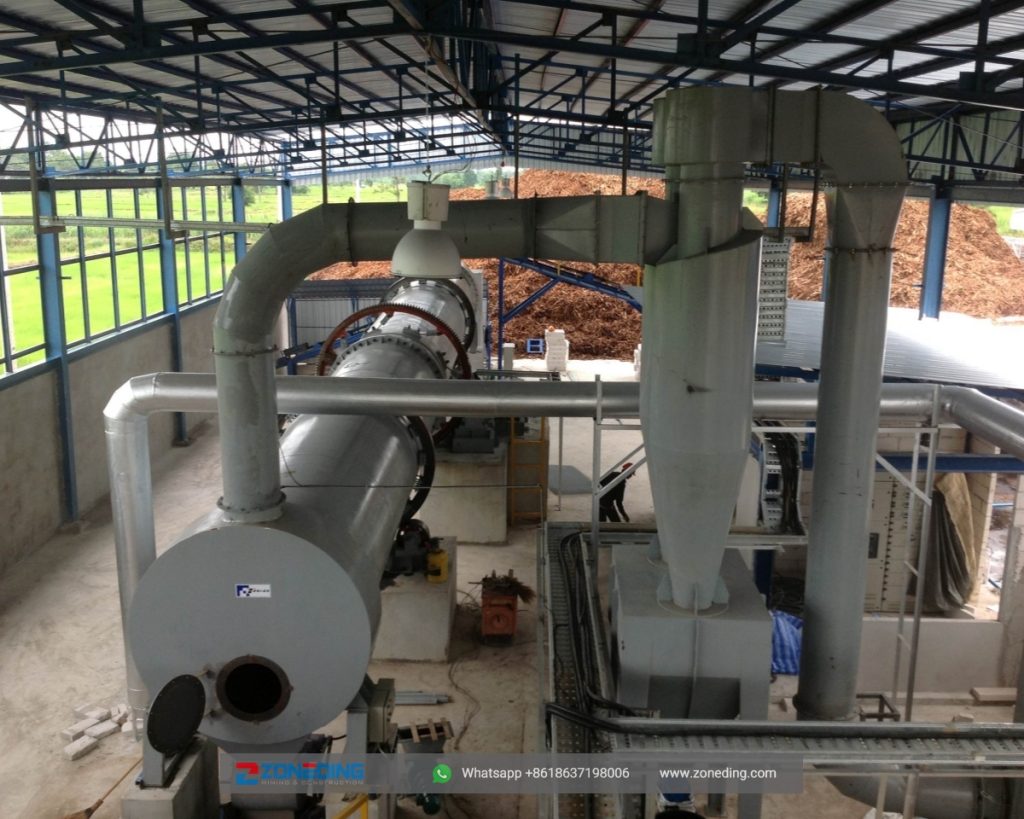
Dust is captured by an air pollution control system, typically a cyclone followed by a baghouse filter. An induced draft fan pulls the hot, dusty air out of the dryer and into the cyclone, which spins out larger particles. The air then goes to the baghouse, where a series of fabric filters capture the remaining fine dust before the clean air is vented to the atmosphere.
When drying materials like coal or biomass, safety is paramount. Essential systems include temperature sensors at the inlet and outlet to prevent overheating, spark detection and suppression systems that can spray water if an ember is detected, and an emergency bypass damper that can vent hot gases away from the baghouse in an over-temperature event.
You calculate ROI by comparing the total cost of the drying system to the financial benefits. The benefits include: money saved on fuel due to high efficiency, the value of reduced scrap and rejected products, increased revenue from higher overall plant throughput, and lower maintenance costs from a well-built machine. For many of our clients, the savings from eliminating just one week of bad production can be a significant portion of the dryer’s cost.
Related Products
Buy industrial gypsum dryer for sale. Efficiently remove moisture from gypsum rock & powder. Improve product quality & processing speed.
Rotary cooler for sale. Efficiently cool hot materials discharged from kilns & dryers. Improve process speed & material quality.
Buy industrial rotary kiln for sale. Achieve efficient high-temperature thermal processing, calcining, roasting & drying of minerals, ore, cement & more.
Find high-efficiency sludge dryers for sale. Reduce sludge volume, cut disposal costs, and improve handling. Ideal for municipal & industrial applications.
Discover high-performance aggregate and sand dryers for sale. We offer triple-pass and rotary drum models for efficient moisture removal. Get a quote today!
Looking for a high-efficiency triple-drum rotary dryer? Saves energy, space, and cost; suitable for drying sand, coal, and biomass. Rugged and reliable.
Purchase an industrial bentonite dryer suitable for various applications such as drilling mud, cat litter, and foundry work. Achieve optimal moisture content and uniform drying.
Specialized Coal Dryer machines for power generation, coking, and briquetting. Improve fuel efficiency, reduce transport costs & enhance combustion.
Professional slurry dryer manufacturer with CE/ISO certification. Customizable 5-50t/h capacity, 35% energy saving. Get instant technical specs download.
Professional slag dryer manufacturer with CE/ISO certification. Energy-saving 30%, global delivery to 50+ countries. Get custom solutions for mining waste processing.
loading…
已经是到最后一篇内容了!