Search the whole station Crushing Equipment
The Rotary Kiln is a very important machine in many big industries. It uses very high heat to change materials. People use it for making cement, processing minerals, and treating waste. It is a big, rotating cylinder.
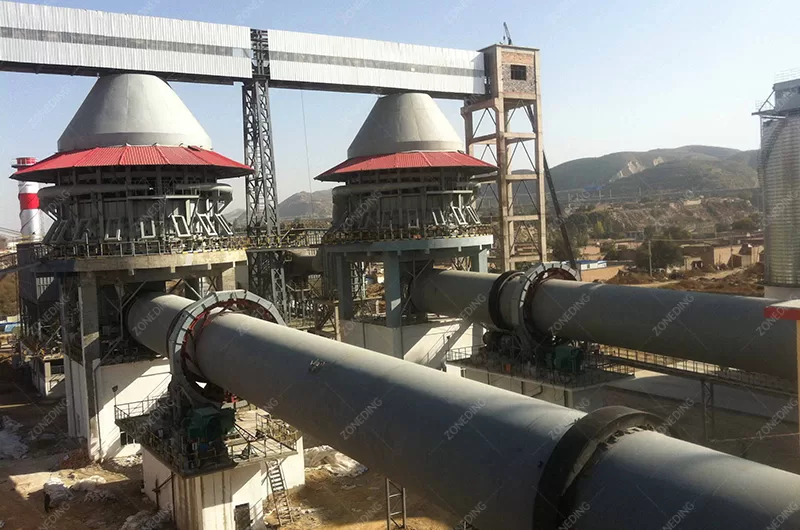
A Rotary Kiln is a piece of heavy-duty equipment. It looks like a very long, large cylinder. This cylinder is placed at a small angle. It turns slowly. It handles materials that need high heat treatment. The high heat causes physical or chemical changes in the material. This process is often called calcining, drying, or sintering. It is a continuous process. Material goes in one end. It moves through the kiln. It comes out the other end changed by the heat.
I see Rotary Kilns as the “heart” of many processes. This is because they are central to the production of key materials. Cement is a good example. Making cement clinker needs very high temperatures. The Rotary Kiln does this job. Without the kiln, you cannot make cement. Many mineral processing steps also need high heat. Removing moisture or changing mineral structure happens in a kiln. The Rotary Kiln provides the controlled high-temperature environment needed for these important reactions. It handles large amounts of material constantly. This makes it essential for large-scale industrial production. It is a critical part of the plant. If the kiln stops, the whole production stops. This is why it is often called the “heart” of the process.
The “alchemy” inside a Rotary Kiln is about using heat and movement to change material. The basic idea is simple. You feed raw material into the higher end of the tilted cylinder. As the cylinder rotates, the material slowly moves down towards the lower end. Hot gas flows through the kiln. This gas can flow in the same direction as the material (co-current) or in the opposite direction (counter-current). Counter-current flow is more common for processes like calcining cement. It provides better heat transfer efficiency.
Inside the kiln, the temperature is very high. It can reach over 1400 degrees Celsius (2550 F) for cement production. Different zones inside the kiln have different temperatures. As the material moves, it goes through these zones. First, it dries. Then, water that is part of the material’s chemical structure is removed. Finally, the material undergoes high-temperature reactions like calcining or sintering. The rotating action of the kiln helps the material mix and tumble. This ensures even heating of all particles. It also moves the material along the length of the kiln. The slope and the rotation speed control how fast the material moves.
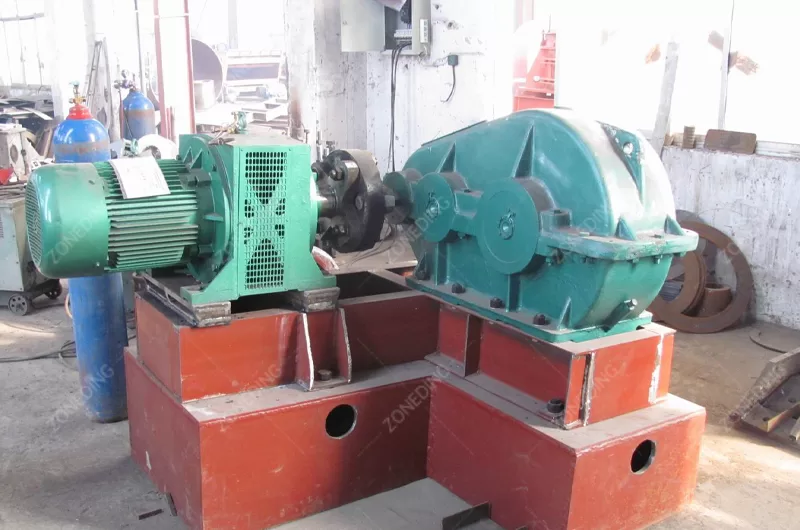
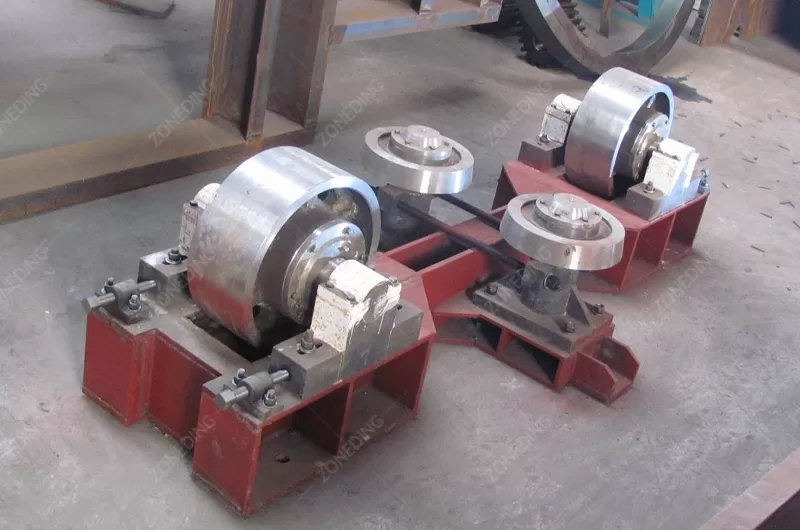
The structure of a Rotary Kiln is robust. It has a steel shell. This shell is lined with refractory bricks. The refractory bricks protect the steel shell from the intense heat and wear. They insulate the kiln to keep heat inside. The kiln cylinder is supported by riding rings or tires. These rings rest on support rollers. The rollers carry the weight of the kiln and the material. A drive system (motor and gearbox) turns the kiln. There are seals at the inlet and outlet ends to minimize air leakage. These seals help control the airflow and heat inside. Fuel is burned at the lower end of the kiln to create the hot gas. The hot gas moves through the kiln, heating the material. The changed material (like cement clinker or calcined ore) comes out the lower end. The hot gas exits the upper end.
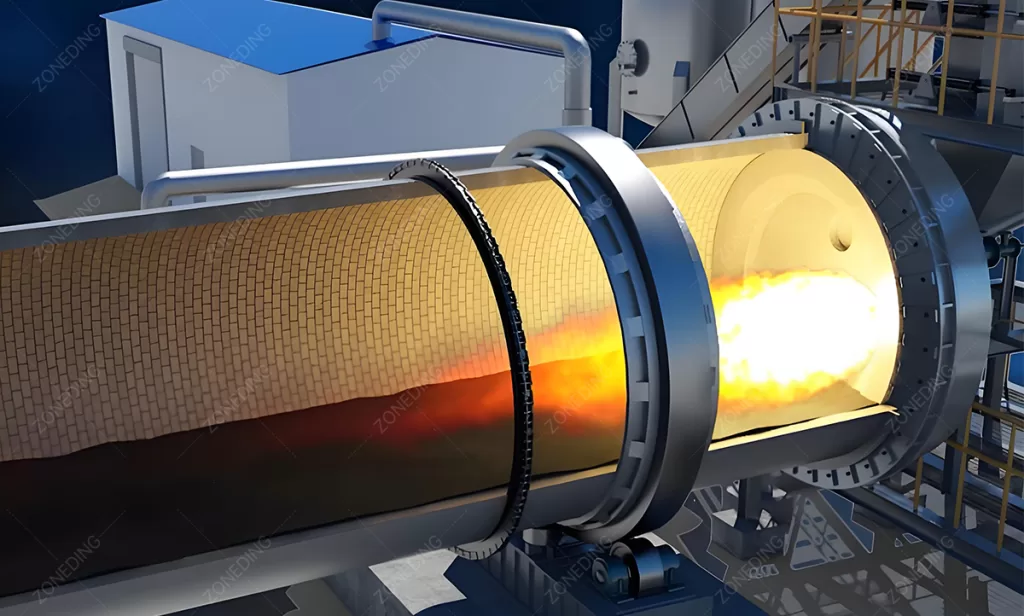

The Rotary Kiln is famous for making cement. But its use goes far beyond that. Any industry needing to heat large volumes of material to high temperatures often uses a Rotary Kiln. Its ability to handle material continuously under controlled heat makes it versatile.
In the mineral processing world, Rotary Kilns are used for many things. They dry wet ores or concentrates before further processing like flotation or magnetic separation. They calcine minerals to remove impurities or change their chemical state. For example, processing certain iron ores might involve calcining. Drying bauxite for aluminum production needs high heat. Treating some gold ores might use a kiln. Rotary kilns are also used to regenerate activated carbon used in gold recovery processes. They are used in processing phosphates, titanium dioxide, and lightweight aggregates like expanded clay (LECA). My products like Ball Mills, Flotation Machine, and Magnetic Separator are often part of the plant that feeds into or receives material from a Rotary Kiln in mineral processing.
In the chemical industry, Rotary Kilns are used for drying chemicals, performing high-temperature reactions, or incinerating specific chemical wastes. They are used in the production of lime, soda ash, and various pigments. The ability to handle solids and powders at high temperatures is key. Environmental applications are also growing. Rotary Kilns are used to incinerate hazardous waste. The high temperatures destroy dangerous compounds safely. They are used in soil remediation to clean contaminated soil by heating it. They can also be used to pyrolyze materials, turning waste into usable energy or materials. The uniform heating and controlled atmosphere inside the kiln are great for these tasks.
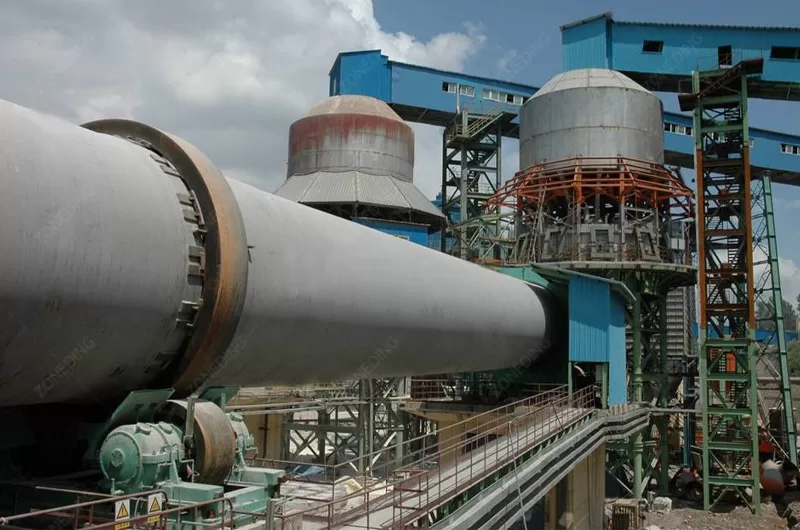
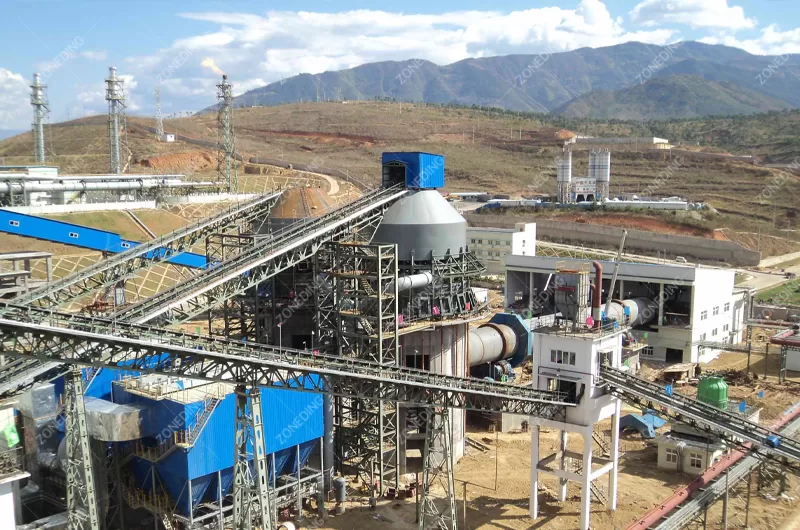


Choosing the right Rotary Kiln is very important. It affects how well it works, how much it costs to run, and the quality of the product. The material you process is the main factor. What is the material? What is its moisture content? How does it behave when heated? What final product do you need?
The first big choice is between a dry process kiln and a wet process kiln. This depends on the raw material’s moisture. If the material is fed as a dry powder, you use a dry process kiln. This is common in modern cement plants. If the material is a wet slurry, you use a wet process kiln. Wet kilns are often longer to dry the material first. Dry kilns are generally more energy efficient because they do not need to evaporate as much water. The size of the kiln (length and diameter) depends on the required throughput and the material’s heating needs. Materials that need more time at high temperature require a longer kiln. Higher production volumes need a larger diameter and potentially longer kiln. The shape of the kiln lining, the number of support piers, and the internal structures (like lifters in drying zones) also vary based on the material and process.
We consider your specific material properties. We look at your desired output (product type, quality, capacity). We analyze your budget and energy costs. We help you select the kiln type (wet/dry). We determine the correct size (length and diameter). We specify the right internal design and refractory lining. For example, calcining limestone for lime production might use a different kiln design than calcining bauxite. Cement kilns have specific preheating and cooling systems often integrated. The design is optimized for your specific application. Getting this choice right at the start saves you problems and money later.


| Dimension(m) | Capacity(t/d) | Slope(%) | Catch wheel | Support number | Power(kw) | Rotate speed(r/min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Φ2.8/2.5×44 | 300 | 3.5 | Mechanical | 3 | 55 | 0.445-2.22 |
| Φ3.2×50 | 1000 | 3.5 | Hydraulic | 3 | 160 | 0.36-3.57 |
| Φ3.5×54 | 1500-1800 | 4 | Hydraulic | 3 | 220 | 0.39-3.9 |
| Φ4×60 | 2500 | 4 | Hydraulic | 3 | 315 | 0.41-4.07 |
| Φ4.8×74 | 5000 | 4 | Hydraulic | 3 | 630 | 0.35-4 |
| Φ6.0×95 | 10000 | 4 | Hydraulic | 3 | 950×2 | Max 5 |
| Dimension(m) | Capacity(t/d) | Slope(%) | Catch wheel | Support number | Power(kw) | Rotate speed(r/min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Φ3.1/2.5×78 | 200 | 3.5 | – | 4 | 90 | 0.5-1.5 |
| Φ3.0×88 | 260 | 3.5 | – | 5 | 90 | -1.74 |
| Φ3.0×100 | 300 | 4 | – | 5 | 110 | -1.74 |
| Φ3.3×118 | 400 | 3.5 | Hydraulic | 6 | 125 | -1.45 |
| Φ3.3×125 | 500 | 3.5 | Hydraulic | 6 | 160 | -1.45 |
| Φ3.5×145 | 700 | 3.5 | Hydraulic | 6 | 90×2 | -1.38 |
A Rotary Kiln uses a lot of energy, mostly fuel for heating and electricity for turning. People call it a “money-burning” machine because of its high operating costs. Making it more efficient is key to profitability. Improving energy efficiency means using less fuel to process the same amount of material.
One major way to save energy is through heat recovery. The hot gas leaving the kiln still contains a lot of heat. This heat can be used to preheat the incoming raw material. This is done in preheater towers for dry process cement kilns. The material falls down through rising hot gas. This transfers heat from the gas to the material before it enters the kiln. This significantly reduces the energy needed inside the kiln. Similarly, the hot product leaving the kiln (like cement clinker) is very hot. This heat can be used to preheat the combustion air for the burner. This makes the fuel burn more efficiently. Using systems like grate coolers for clinker helps recover this heat.
Maintaining the kiln properly is also crucial for efficiency. Good seals at the kiln ends prevent cold air leaks. Cold air entering the kiln cools down the process and wastes energy. The refractory lining needs to be in good condition. Damaged or thin lining allows heat to escape through the steel shell. This wastes energy. Optimizing the fuel combustion is important. Using the right amount of air ensures the fuel burns completely and efficiently. Controlling the material feed rate and kiln rotation speed helps maintain stable process conditions. This leads to better heat transfer and lower energy use. Newer kiln designs often include advanced control systems and optimized heat exchange features to improve efficiency. We focus on designs that incorporate these energy-saving features. For instance, integrating a proper preheater system is vital for dry process efficiency.
A Rotary Kiln works under extreme conditions: very high temperatures and constant movement of abrasive material. Ensuring it runs continuously and reliably is a major challenge. Proper maintenance is essential. The most critical component is the refractory lining. This layer of special bricks protects the steel shell from the heat. Refractory wears out over time from the heat, chemical attack, and abrasion from the material. Regular inspections are needed to check the condition of the bricks. Worn bricks must be replaced quickly. Losing refractory can damage the steel shell, leading to expensive repairs and long shutdowns.
The steel cylinder itself needs maintenance. The riding rings and support rollers carry huge loads. They need regular lubrication and alignment checks. The shell can sometimes deform or develop cracks due to heat stress and load. Monitoring the shell temperature helps detect problems early. The drive system (motor, gearbox, couplings) also requires regular inspection and lubrication. The seals at the ends need to be maintained to prevent air leaks.
Common problems include refractory failure, shell cracks, roller and tire wear, and drive system issues. Dust buildup inside the kiln or in the connected systems (like cyclones or baghouses) can also disrupt operation and cause blockages. Regular cleaning is important. A good maintenance plan includes daily checks, weekly inspections, monthly lubrication, and planned shutdowns for major refractory relining or mechanical repairs. Having a stock of critical spare parts, especially wear parts like refractory bricks and seal components, is vital. Training your staff on kiln operation and maintenance is also crucial. They need to understand how to monitor the kiln and spot early signs of trouble. We provide guidance on maintenance schedules and spare parts for our kilns.
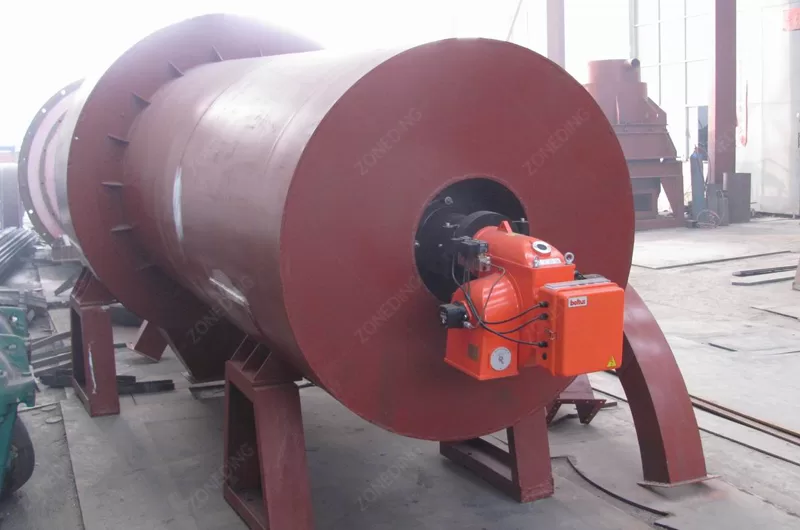
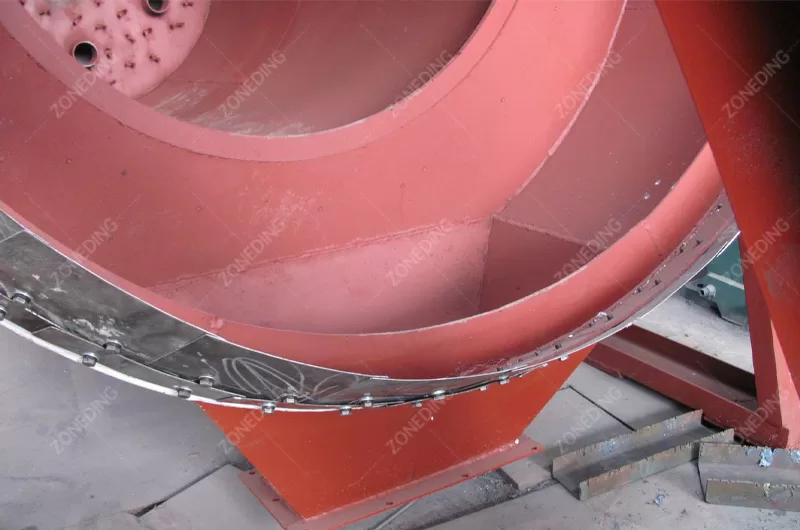
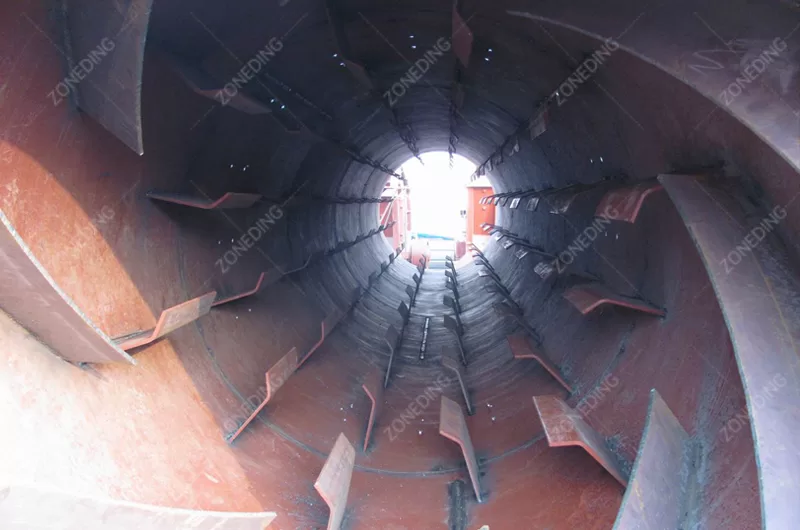
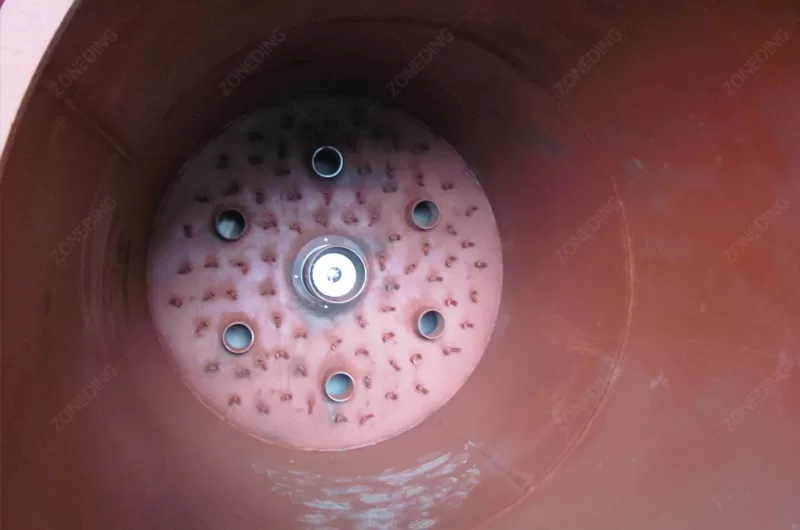






Rotary Kilns produce hot gases as a result of combustion and material processing. These gases, often called flue gas or tail gas, contain dust particles and sometimes harmful gases (like SO2, NOx, or other pollutants depending on the material and fuel). Environmental regulations around the world are getting stricter. Treating the kiln’s tail gas is necessary to comply with these rules and be environmentally responsible.
Dust is a common problem. Kiln exhaust gas carries fine particles from the material and fuel. Different technologies are used to remove dust. Cyclone separators use centrifugal force to remove coarser particles. Baghouses (fabric filters) use large bags to filter out fine dust. Electrostatic precipitators (ESPs) use electric charge to collect dust particles. Baghouses and ESPs are very effective at removing fine dust and are often required to meet strict particulate emission limits.
Removing harmful gases requires other technologies. Sulfur dioxide (SO2) comes from sulfur in the fuel or raw material. Flue gas desulfurization (FGD) systems are used to remove SO2. Wet scrubbing systems use a liquid (like a lime slurry) to absorb the SO2 from the gas. Nitrogen oxides (NOx) are formed at high temperatures during combustion. Reducing NOx emissions can involve modifying the combustion process (e.g., low NOx burners) or using flue gas treatment methods like selective catalytic reduction (SCR) or selective non-catalytic reduction (SNCR). Some processes might also need to remove other pollutants like heavy metals or dioxins, requiring specialized filters or scrubbers. The specific tail gas treatment system depends on the kiln application, the fuel used, the raw material, and the local environmental regulations. Designing and installing the right flue gas purification system is a complex task. It requires expertise in both the kiln process and environmental control technologies.
Investing in a Rotary Kiln is a big financial commitment. It is one of the most expensive pieces of equipment in a processing plant. You need to look at both the upfront cost and the costs to run it over many years. The initial purchase price for the kiln itself is substantial. This cost depends on the size of the kiln (length and diameter), the materials used for construction (steel quality, refractory type), the complexity of the design (e.g., integrated preheaters, coolers), and the supplier. A large industrial kiln can cost millions of US dollars.
But the kiln is just one part of the system. You also need to consider the cost of auxiliary equipment. This includes the feeding system, the burner system, the drive system, the support rollers and piers, the discharge system, and importantly, the flue gas treatment system. These auxiliary systems add significantly to the total capital cost. Installation costs are also high because these machines are large and complex to set up. Civil works for foundations and structures are needed.
Long-term operating costs are also significant. Fuel cost is often the largest single operating expense. This depends on the type of fuel (coal, gas, oil), its price, and the kiln’s energy efficiency. Electricity cost for running motors and fans is another major expense. Maintenance costs, especially for replacing refractory lining and other wear parts, are substantial. These parts need regular replacement due to the high heat and abrasion. Labor costs for operating and maintaining the kiln are also part of the picture. You also have costs for environmental compliance, such as running the flue gas treatment system and monitoring emissions. To evaluate the investment, you must calculate all these costs over the expected life of the kiln. Compare the total cost of ownership to the potential revenue from the product it produces and the cost savings (e.g., from processing raw materials more efficiently). Getting accurate figures for your specific material and location is key. We provide detailed cost breakdowns and can help you estimate the long-term economic performance.
Selecting the right Rotary Kiln supplier is very important. It is like a big test. You need a partner you can trust. They need strong technical skills and good service. This is not a machine you buy off the shelf without support. Look for a supplier with deep experience in building Rotary Kilns for your specific industry (cement, mining, chemical, etc.). Different applications require different kiln designs. We have been making heavy machinery since 2004 and understand various mineral processing needs.
Check their engineering team’s strength. Do they have engineers who understand thermodynamics, material science, and structural design for high-temperature applications? Our 15 professional engineers are key here. They design reliable and efficient kilns. Ask about their manufacturing capabilities. Do they have a large factory with the right equipment to build such big, heavy machinery accurately? Our 8000 square meter factory is equipped for this. Can they provide case studies or references for similar kilns they have supplied? Seeing their machines working successfully for other customers gives you confidence. We have supplied equipment to over 120 countries, showing our global reach and experience.
Service is crucial. A good supplier provides comprehensive service. This includes helping you select the right kiln model based on your material testing and capacity needs. They should provide detailed engineering design and layout plans for your plant. They must ensure quality during manufacturing. After the kiln is built, they should supervise the installation and commissioning at your site. This is complex machinery; you need expert help to get it running correctly. They should provide training for your operators and maintenance staff. This ensures your team knows how to run the kiln safely and efficiently. Finally, they must offer reliable after-sales support, including readily available spare parts and technical assistance for troubleshooting. We offer these full-service capabilities. We provide complete solutions.
Q1: What is the typical lifespan of a Rotary Kiln?
A1: With proper design, construction, operation, and maintenance, a Rotary Kiln’s steel shell can last for many decades, often 20-30 years or even longer. The refractory lining needs replacement periodically.
Q2: Can a Rotary Kiln handle different types of fuel?
A2: Yes, Rotary Kilns are designed to use various fuels including coal powder, natural gas, oil, and sometimes alternative fuels like waste-derived fuels. The burner system is key to handling different fuels.
Q3: How is the temperature controlled inside the kiln?
A3: Temperature is controlled by adjusting the fuel feed rate and the airflow for combustion. Modern kilns also use advanced sensors and automatic control systems to maintain desired temperature profiles in different zones.
Buy industrial gypsum dryer for sale. Efficiently remove moisture from gypsum rock & powder. Improve product quality & processing speed.
Rotary cooler for sale. Efficiently cool hot materials discharged from kilns & dryers. Improve process speed & material quality.
Find high-efficiency sludge dryers for sale. Reduce sludge volume, cut disposal costs, and improve handling. Ideal for municipal & industrial applications.
Discover high-performance aggregate and sand dryers for sale. We offer triple-pass and rotary drum models for efficient moisture removal. Get a quote today!
Looking for a high-efficiency triple-drum rotary dryer? Saves energy, space, and cost; suitable for drying sand, coal, and biomass. Rugged and reliable.
Purchase an industrial bentonite dryer suitable for various applications such as drilling mud, cat litter, and foundry work. Achieve optimal moisture content and uniform drying.
Specialized Coal Dryer machines for power generation, coking, and briquetting. Improve fuel efficiency, reduce transport costs & enhance combustion.
Professional slurry dryer manufacturer with CE/ISO certification. Customizable 5-50t/h capacity, 35% energy saving. Get instant technical specs download.
Professional slag dryer manufacturer with CE/ISO certification. Energy-saving 30%, global delivery to 50+ countries. Get custom solutions for mining waste processing.
This mineral powder dryer is specifically designed for use with mineral concentrates, iron ore powder, and metallurgical slag. It ensures uniform drying, improving product quality and recovery rates.
loading…
已经是到最后一篇内容了!
We use cookies to ensure that we give you the best experience on our website. If you continue to use this site we will assume that you are happy with it.
Privacy Policy