Search the whole station Crushing Equipment
Sawdust dryer applys in pellet sawdust or powder sawdust. Wet materials are sent continuously into the drum through a screw conveyor and then get separated and pushed by the high-speed hot flow. The moisture in wet materials will go away in this process and then we get powder or pellet dry materials.
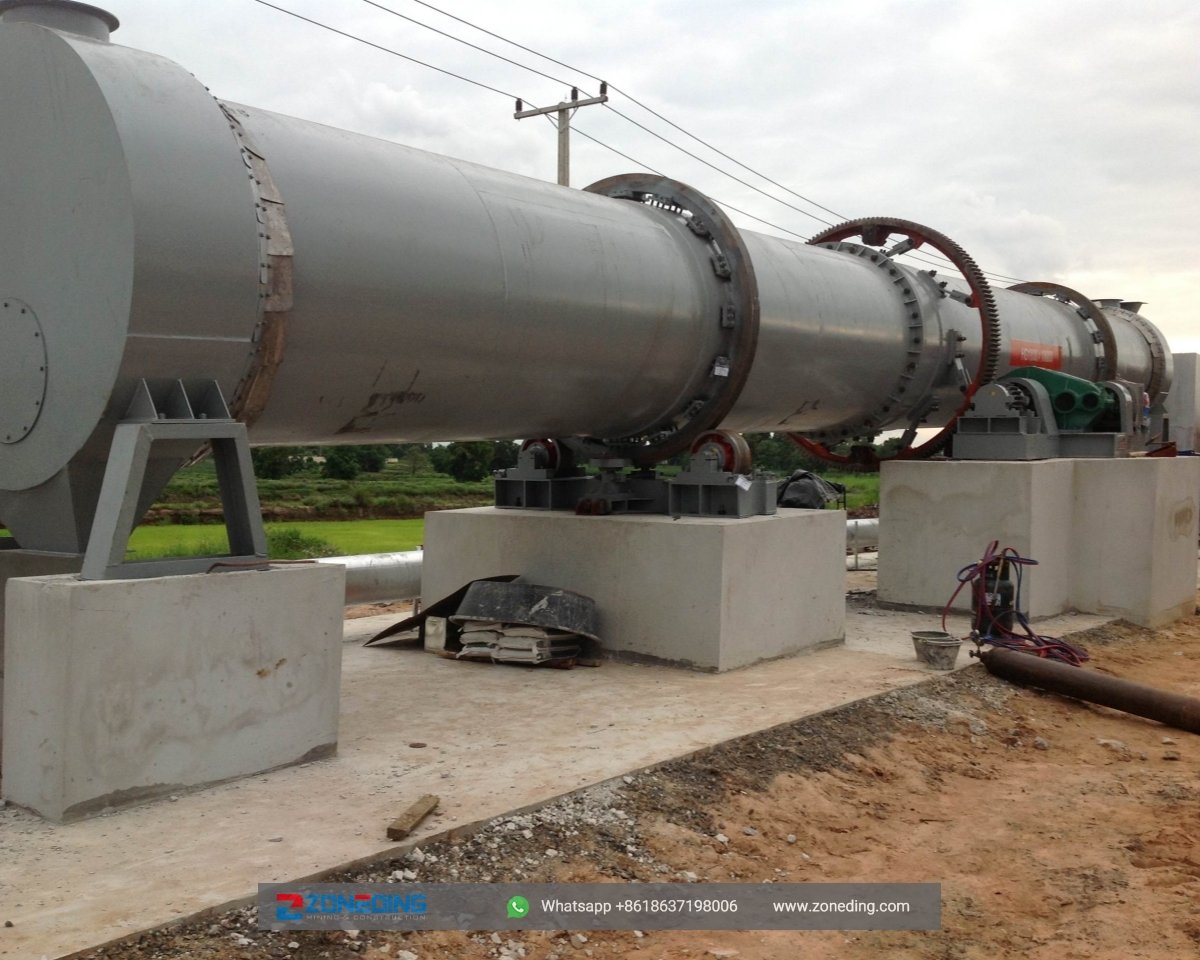
Sawdust dryer is one type of rotary dryer that is specially for drying sawdust, wood chips, straw and charcoal, etc. It has high drying intensity, short drying time, large production capacity, high efficiency, small occupied area, easy operation and maintenance, etc. It is also as sawdust drying machine or sawdust rotary dryer. Mainly, there are two types of sawdust dryer machine:airflow sawdust dryer and three-channel dryer. The latter applys in the sawdust drying process.

Sawdust consists of the fine particles of wood left over from sawing, grinding, or sanding wood. It is a a byproduct of many industrial processes. The character of sawdust can vary greatly. It can be wet or dry, coarse or fine, and made from different wood species. These variations are very important when it comes to drying it effectively.
Dry sawdust is an incredibly versatile raw material. While its most well-known use is for making wood pellets for fuel, it has many other valuable applications:
You must dry sawdust to make it useful and valuable. Raw, wet sawdust has very limited use. It is heavy, difficult to handle, and will rot quickly. Drying the sawdust unlocks its potential and provides several key benefits:
The enemy is “case hardening,” not just moisture. You can have sawdust that tests “dry” on average but is a disaster. This happens when you use excessively high temperatures. The outside of each wood particle flash-dries, forming a hard shell that traps moisture inside. When this particle enters a high-pressure pellet die, the trapped steam can flash and cause the pellet to crack or explode. A slower, lower-temperature drying process, which a professional biomass dryer provides, produces a consistently dry particle that is far safer and more effective.
Sawdust has unique characteristics that make it challenging to dry correctly:
A sawdust dryer is an industrial machine specifically designed to handle the unique challenges of drying wood particles. It is a complete system engineered to heat the sawdust, evaporate the water, and separate the dry product from the air stream safely and efficiently. The two main types are the rotary drum dryer and the airflow dryer.
The primary application of a sawdust dryer is to prepare the material for pelletization. This is the largest market. Any facility that aims to produce biomass fuel pellets needs a reliable dryer. Other key applications include:
Sawdust refers to as the dust, chips, shavings and other materials left when processing wood. Dried sawdust applys widely as fuel, filler, etc. As a result, sawdust dryer machine has many different applications as follows:
Fuel processing: dried sawdust when briquetted is the key raw material in the fuel industry, like in heating supply system, power plant and so on;
Furniture industry: sawdust rotary dryer applys to dry the wet sawdust to a certain humidity, which is for the shaving board making, plywood making, etc.
Paper Making Industry: dried sawdust can be the raw material when make paper, therefore, this sawdust drying machine plays an initial part;
Edible fungus cultivation: the raw material sawdust can be to cultivate mushrooms, fungus mushrooms, needle mushroom and agaric mushroom.



While it is called a sawdust dryer, this machine is a versatile biomass dryer. It can process a wide range of similar fibrous, organic materials:
The key is that the material is small enough to be tumbled in a drum or conveyed in an air stream.
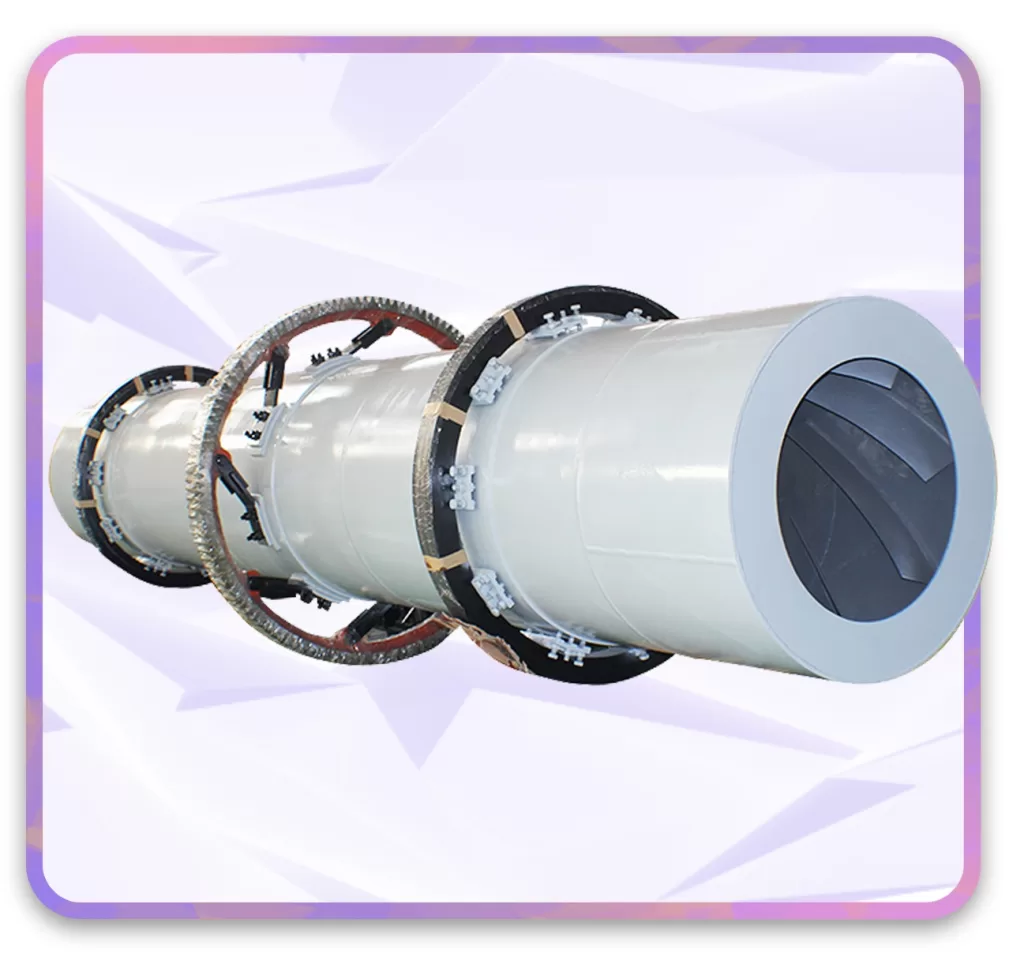
A professional sawdust dryer system is more than just a drum. It is a carefully integrated set of components. The structure includes:
Sawdust Dryer has key components: a heating furnace, inlet, rotating cylinder, filtering cylinder, conveying pipe, cooling tube and the outlet.
Small occupied area, easy construction and maintenance, low drying cost. The material is highly dispersed in the airflow dryer; the particle surface is the effective drying area;
Strong drying strength, short drying time, high processing capacity, high thermal efficiency, non-binding water heat efficiency is up to 60%;
Wide scope of applications. The operating parameters can be changed according to the requirements of different customers;
Long service life. The cylinder rolls stably, thus, wearing is reduced.
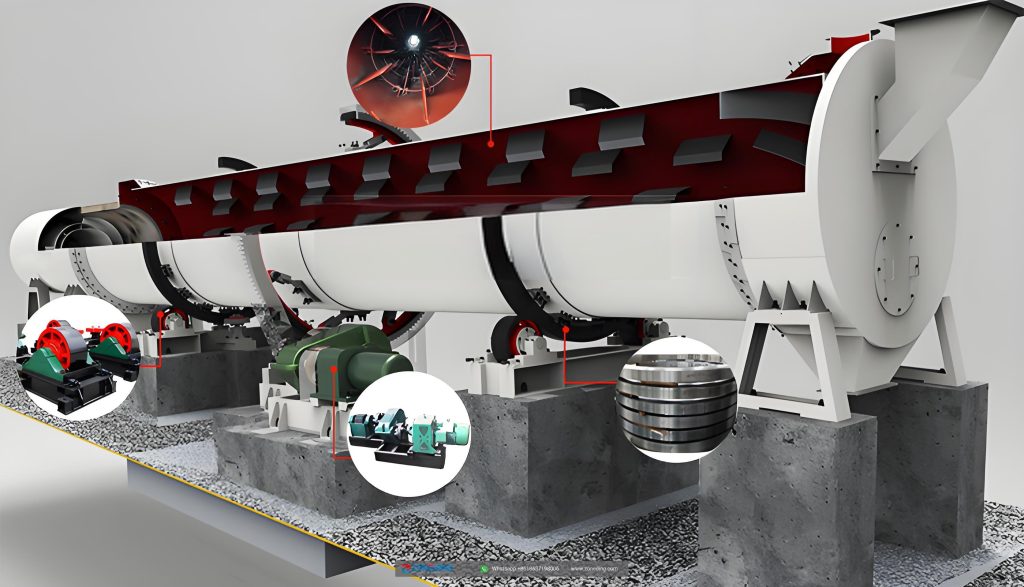
The working principle depends on the type of dryer. In a rotary dryer for biomass, wet sawdust is fed into a large, rotating drum. Internal “lifters” pick up the material and drop it through a stream of hot gas from the furnace. The material slowly tumbles its way to the discharge end.
One critical aspect of the process is managing volatile gases. Your dryer can become a tar factory, which is trying to burn your plant down. When sawdust is heated, it releases flammable wood gases (VOCs). If you see a “blue haze” in your exhaust, your inlet temperature is too high. You are vaporizing the highest-energy part of the wood and sending it out the stack. This vapor then condenses in your ductwork as a sticky, flammable tar (creosote). A stray ember can ignite this tar, causing a severe duct fire. The solution is to lower the furnace temperature and increase airflow. The goal is to dehydrate the wood, not pyrolyze it.
1. The sawdust is fully dried in the rotating cylinder;
2. Sawdust is fully dispersed again before entering into the material conveying pipe, so that the evaporation will be faster;
3. The material is boiling in the tube, the hot air and material will fully contact with each other to complete the drying process.

Faced with numerous changes and threats, Zoneding keeps on the research of how to increase the efficiency of the sawdust dryer and finds some tips.
1>> Replace the spiral conveying blades at the feeding end with 6mm steel triangular stiffened plates. It is to lower the sawdust speed in the high-temperature zone and to make a maximum utilization of the heat.
2>> Build central X-shaped lifting blades to prolong the residence time of the material and improve the heat transformation;
3>> Change the angle of the feeding tube. With the standard of not to influence the feeding efficiency, lift the blanking cylinder as much as possible. The top of the lifted tube shall not touch the material retaining ring. The part of the tube inside the cylinder shall be not too long and the material falls within the 200mm of the retaining ring. Thus, a material screen is formed and heat transformation is enhanced.
A sawdust dryer machine price can range from $40,000 for a small system to over $600,000 for a large-scale industrial plant. However, the purchase price is not the most important cost. The unseen cost is product loss, not fuel. Everyone obsesses over the fuel bill. But in a poorly designed system, the value of the product you lose up the smokestack can be far greater.
Dry sawdust is extremely light. If the air velocity inside your dryer is too high, it acts like a vacuum cleaner. It will carry your lightest particles—the “fines”—right past the cyclone and into your pollution control system. It is not uncommon for a poorly designed system to lose 10-15% of its total product mass this way. That is 10-15% of your profit vanishing into thin air. A properly sized dryer with a high-efficiency cyclone is not a cost; it is an investment in yield.
Choosing the right dryer is the most critical decision you will make. The great secret is that the dryer must match your moisture, not just your material. This single rule determines the type of dryer you need.
Using the wrong type is a recipe for disaster. If you try to use an airflow dryer for very wet sawdust, the material is too heavy to be picked up by the air. It will just sit in a wet, smoldering pile at the bottom of the duct. Conversely, using a huge rotary drum dryer for low-moisture sawdust is a massive waste of fuel and capital, and the long residence time risks over-drying and creating fires.
At ZONEDING, we design our biomass drying systems for profit, safety, and longevity. We go beyond the basics because we know the risks and opportunities of sawdust drying.
Maintaining your sawdust dryer is not just about longevity; it is a critical safety discipline. A sawdust dryer will eventually have a fire. Proper maintenance determines whether it’s a minor incident or a total plant loss. Here are the most important steps:
How do I dry sawdust for pellets?
First, determine your sawdust’s moisture content. If it is over 45%, you need a rotary drum dryer. If it is under 45%, an airflow dryer is better. The goal is to achieve a consistent final moisture content of 10-15% with a low-temperature process to avoid case hardening.
What is the best way to control a sawdust dryer?
The best way is with an automated PLC control system. It should monitor the inlet temperature, the outlet temperature, and the exhaust gas oxygen levels. The system can then automatically adjust the feed rate and burner output to maintain a stable outlet temperature, which ensures a consistent final product moisture content.
How is a fire in a sawdust dryer prevented?
Prevention involves three steps: 1) Proper operation (not too hot, to prevent tar buildup). 2) Proper design (no leaky airlocks, minimal horizontal ducts). 3) Active protection systems, such as spark detection and water deluge systems, which are the professional standard.
Why does my dried sawdust have dark particles?
Dark or scorched particles mean the material is staying in the hot zone for too long or the inlet temperature is too high. This over-drying not only damages the product but also significantly increases the risk of fire.
How much maintenance does an industrial wood chip dryer require?
Daily maintenance involves checking lubrication points and visually inspecting for any issues. Weekly, you should open clean-out doors and inspect for tar or dust buildup in the ducts. The most important maintenance is cleanliness. A clean system is a safe system.
Buy industrial gypsum dryer for sale. Efficiently remove moisture from gypsum rock & powder. Improve product quality & processing speed.
Rotary cooler for sale. Efficiently cool hot materials discharged from kilns & dryers. Improve process speed & material quality.
Buy industrial rotary kiln for sale. Achieve efficient high-temperature thermal processing, calcining, roasting & drying of minerals, ore, cement & more.
Find high-efficiency sludge dryers for sale. Reduce sludge volume, cut disposal costs, and improve handling. Ideal for municipal & industrial applications.
Discover high-performance aggregate and sand dryers for sale. We offer triple-pass and rotary drum models for efficient moisture removal. Get a quote today!
Looking for a high-efficiency triple-drum rotary dryer? Saves energy, space, and cost; suitable for drying sand, coal, and biomass. Rugged and reliable.
Purchase an industrial bentonite dryer suitable for various applications such as drilling mud, cat litter, and foundry work. Achieve optimal moisture content and uniform drying.
Specialized Coal Dryer machines for power generation, coking, and briquetting. Improve fuel efficiency, reduce transport costs & enhance combustion.
Professional slurry dryer manufacturer with CE/ISO certification. Customizable 5-50t/h capacity, 35% energy saving. Get instant technical specs download.
Professional slag dryer manufacturer with CE/ISO certification. Energy-saving 30%, global delivery to 50+ countries. Get custom solutions for mining waste processing.
loading…
已经是到最后一篇内容了!