Search the whole station Crushing Equipment
Zoneding Machine supplies different types of jigging in mineral processing(such as fixed jig and mobile jig machine), the customized parameters for your requirements.
A Mineral jigging machines is a gravity concentration device that separates particles of different densities by pulsating a water column through a bed of material. This causes denser particles to settle faster and lower, while lighter particles are lifted higher and discharged.
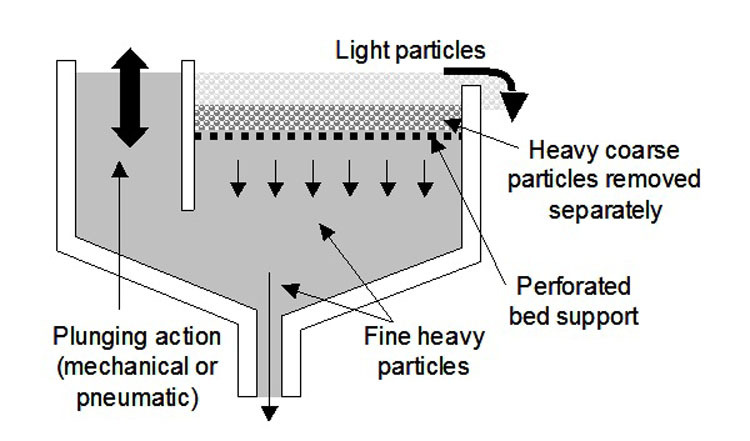
A jig machine, or mineral jig, is a device that separates materials of different densities. The core principle is simple: differences in how fast particles settle in water. Imagine dropping a small stone and a piece of wood into a tube of water; the stone sinks faster. A jig machine does this repeatedly and on a large scale. It uses a pulsating column of water to repeatedly lift a bed of crushed ore. During each pulse, the particles are briefly suspended, allowing the denser (heavier) minerals to sink faster and work their way to the bottom, while the less dense (lighter) waste particles stay near the top. This creates distinct layers, which can then be separated.
Using a jig machinery in your mineral processing circuit offers significant advantages.
The primary benefits are its high efficiency, low operating cost, and environmental friendliness. Unlike other methods that require expensive chemical reagents, a gravity separation jig mainly uses water and electricity, keeping your operational costs down. These machines can handle large volumes of material, making them suitable for both small and large-scale operations. They are also relatively simple to operate and maintain.
At ZONEDING, our jig machines are designed for maximum throughput with minimal power consumption, providing you with a highly economical solution for ore concentration.
The application of a jigging machine is incredibly broad, extending beyond traditional mining. You can use this versatile equipment in many industries. Its ability to effectively separate materials based on density makes it an invaluable tool. Here are some of the most common applications for a jig machine:
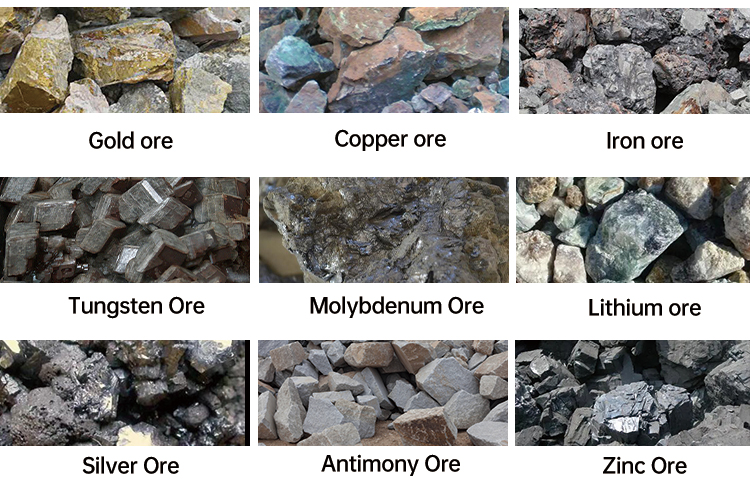
A jigging separator is effective for any mineral that has a significant density difference from its associated waste rock (gangue). It is particularly effective for processing heavy minerals. If you can feel a noticeable weight difference between your target mineral and the surrounding rock, a jig will likely work well. The greater the density difference, the easier and more efficient the separation will be. Common minerals successfully processed with our concentrator machine models include:

A jigger separator is a robust machine built from several key components, each playing a vital role. Knowing the structure helps you understand its operation and maintenance.
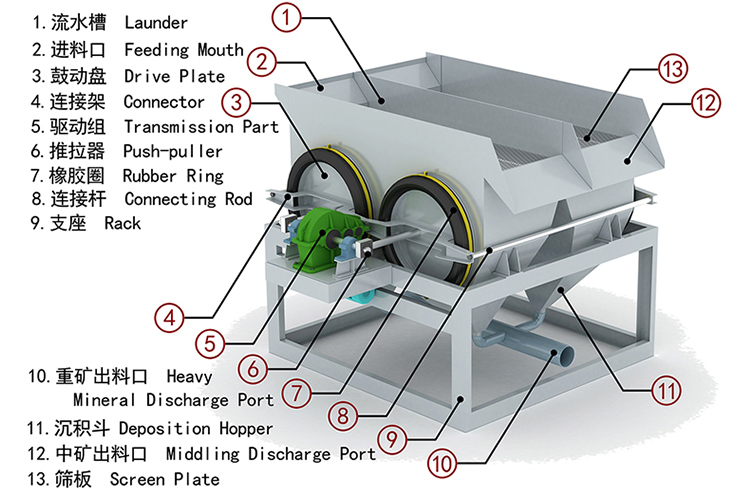
The operation of a jigging separator machine relies on two key processes: pulsation and stratification. Understanding this helps you see how simple yet effective the machine is.
The mineral ore is continuously fed to the screen plate of the jig chamber to form a thick material layer. Rising water is periodically pumped through the sieve plate to loosen the bed, and then the water flows down (or stops rising). During this process, particles with different densities undergo relative transfer. Heavy minerals enter the lower layer, and light minerals move to the upper layer. After being discharged respectively, the concentrate and tailings are obtained.
While all jigging separators operate on the same principle, they use different mechanisms to create the pulsation. The type you choose depends on your specific application and material characteristics.
To get the best results from your jigging separator, you need to understand the factors that influence its performance. The most critical factors are particle size, density difference, and feed rate. A consistent feed is key to stable operation. If the feed rate or material properties change suddenly, the separation efficiency will drop. The particle shape and size distribution also play a huge role. A feed with a very wide range of particle sizes can be difficult to separate in a single pass. In such cases, pre-screening the material into different size fractions before feeding it to the jig can dramatically improve your recovery rates.
Optimizing your jig’s operation is about fine-tuning it for your specific ore. It’s a process of adjustment and monitoring to find the perfect balance. Focus on adjusting the stroke length and frequency. Many operators only adjust the cycles per minute, but the stroke profile—the shape and acceleration of the pulse—is even more important. At ZONEDING, our modern jigs offer advanced controls that allow you to tailor this profile. A short, fast stroke is often better for fine particles, while a long, slow stroke works well for coarse material. Also, carefully control the hutch water flow rate. Too little water will not fluidize the bed properly, while too much will wash away fine, valuable minerals.
Choosing the right jigging separator is a crucial investment decision. The right machine will run efficiently for years, while the wrong one can cause constant headaches. Here is a simple checklist to guide you:
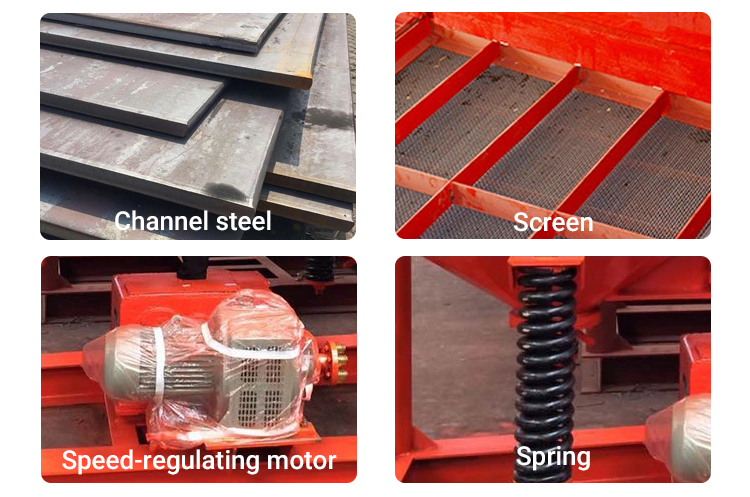
A jigging separator machine is designed for durability, but regular maintenance is essential for long-term performance. The most important maintenance tasks involve checking and replacing wear parts. The screens are subject to constant abrasion and will need to be inspected regularly and replaced when worn. Uneven wear can create holes that let coarse material fall into the hutch, contaminating your concentrate. You should also regularly inspect the drive mechanism, lubricate all moving parts like bearings, and check the rubber diaphragms for cracks or wear. Finally, bed maintenance is critical. Over time, the bed can become compacted, which stops stratification. Regularly scheduled cleaning and re-stratification will keep your machine running at peak efficiency.
| Model | Jig Area (M2) | Stroke (R/Min) | Feeding size (mm) | Hutch Water ( T/H) | Pressure Water (kg/cm2) | Capacity;(T/H) | Power;(KW) | Overall dimensions (mm) | Weight (T) |
| JT0.57-1 | 0.57 | 60-160 | <6 | 1-2 | ≥0.3 | 1-2.5 | 1.5 | 1560x820x1550 | 0.612 |
| JT1-1 | 1.04 | 60-160 | <10 | 2-3 | ≥0.3 | 4-10 | 2.2 | 1322x1190x1915 | 0.9 |
| JT2-2 | 2.28 | 60-160 | <10 | 2-4 | ≥0.3 | 8-15 | 3 | 3225x1550x2150 | 1.637 |
| JT4-2 | 4 | 50-125 | <10 | 4-8 | ≥0.1 | 8-16 | 7.5 | 4240x1990x2750 | 4.6 |
| JT4-2A | 4 | 50-125 | <10 | 4-8 | ≥0.1 | 8-16 | 8 | 4240x1990x2750 | 4.6 |
| JT5-2 | 4.86 | 80-120 | <10 | 4-10 | ≥0.1 | 10-20 | 7.5 | 3940x2006x2580 | 4.6 |
At ZONEDING, quality is built into every step of our process. With experience dating back to 1990, we understand what it takes to build a machine that performs reliably in the toughest conditions. We ensure quality through superior design, high-quality materials, and precision manufacturing. Our team of 15 professional engineers designs each mineral jig for optimal performance based on your specific needs. We operate from an 8,000-square-meter factory equipped with advanced CNC machinery. We use high-wear-resistant steel for all critical components, such as the screens and drive parts. Every machine undergoes rigorous testing before it leaves our factory to ensure it meets our high standards and your expectations.
The cost of a jigging separator machine can vary significantly. The price depends on several factors, including the size and capacity of the machine, its type (e.g., diaphragm vs. air-pulsated), the level of automation, and the materials used in its construction. A small, simple jig for a pilot plant might have a lower initial cost, while a large, high-capacity, fully automated machine for a major mining operation will be a more substantial investment. However, you should always consider the total cost of ownership, not just the purchase price. A well-built, efficient machine from a reputable manufacturer like ZONEDING will save you money in the long run through lower energy consumption, reduced maintenance, and higher mineral recovery rates.
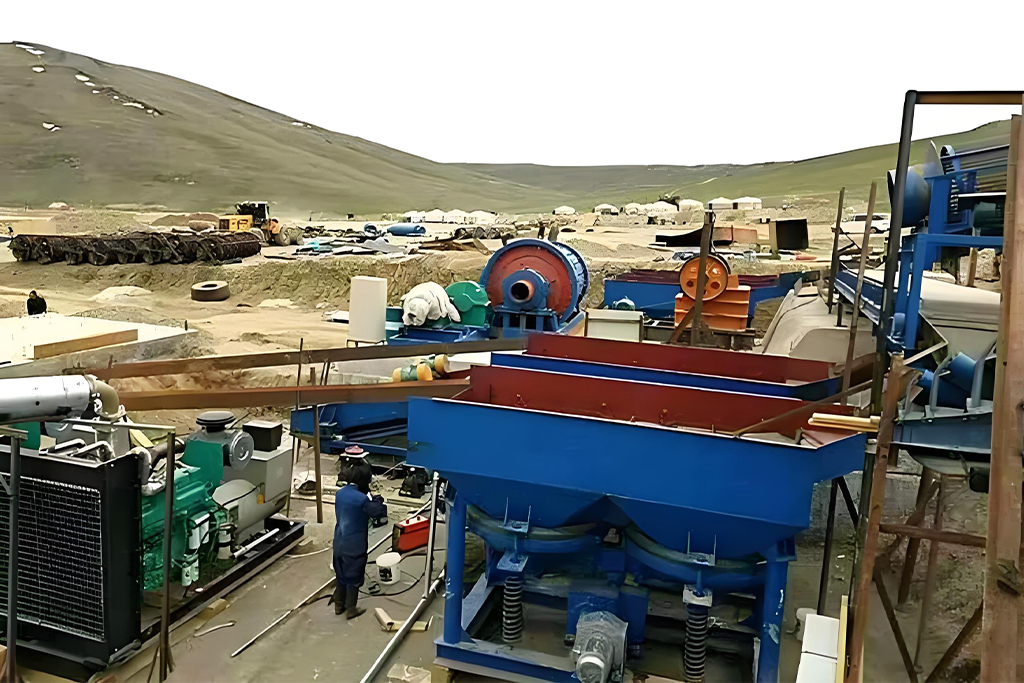
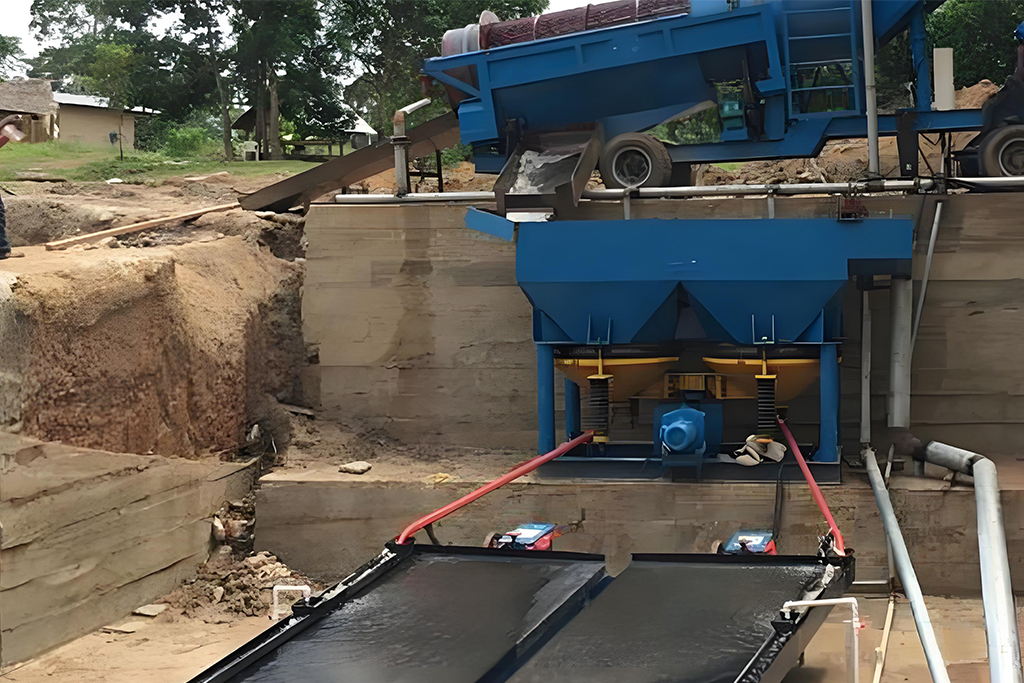
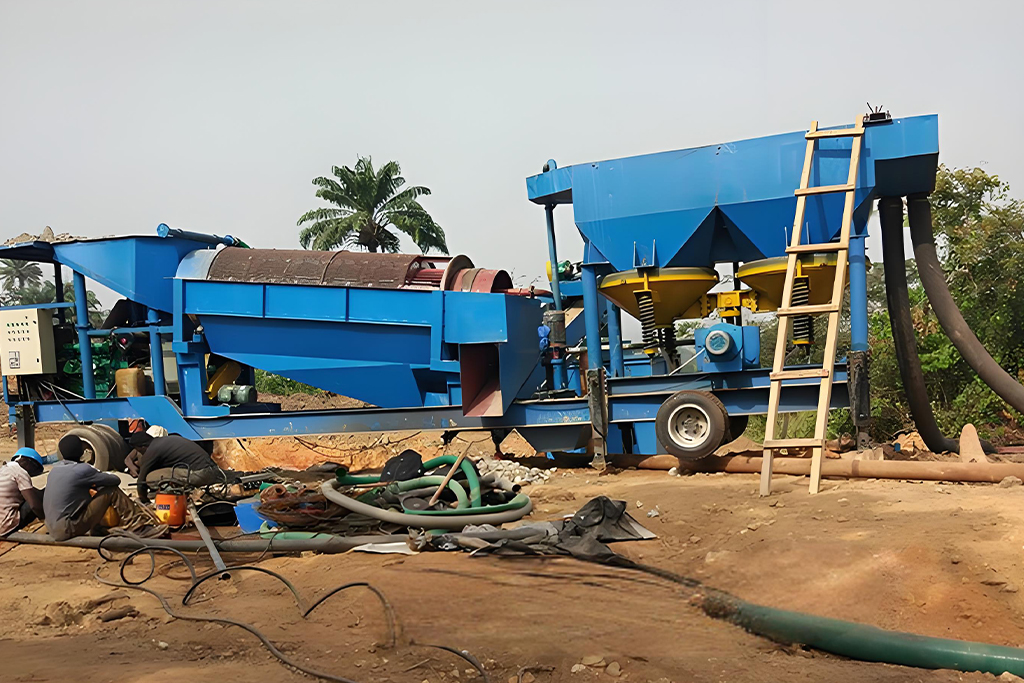



The jigging separator machine is a proven, efficient, and economical tool for mineral processing. Its ability to separate a wide range of minerals using just water and gravity makes it a cornerstone of modern, sustainable mining operations. From understanding its basic working principle to optimizing its performance and choosing the right model, success depends on a solid understanding of the technology and your specific needs.
When you are ready to invest, we strongly recommend partnering with an experienced manufacturer. A good supplier will not only provide a high-quality machine but will also offer expert advice on installation, operation, and maintenance. If you want to improve your mineral recovery rates while keeping costs low, a jigging separator from ZONEDING is an excellent choice.
Ready to boost your mineral processing efficiency? Contact our experts at ZONEDING today for a customized quote and expert consultation!
Your reliable source for high-capacity, heavy-duty ball mills engineered for mining, cement, and fine powder processing.
Zongding Machinery provides advanced ball mills and mineral processing equipment to help mining companies around the world process minerals more efficiently.
the best Ceramic Ball Mill manufacturers and their competitive prices. Our selection offers top-quality mills for various applications at affordable costs.
Efficient flotation machine for mineral processing at competitive prices. Maximum recovery and optimal grade for your mining operations.
A magnetic separator is a device that separates magnetic minerals from nonmagnetic minerals by applying a magnetic field.
Spiral classifiers can grade different particles in ore slurry during the metal beneficiation process as well as deslime and dehydrate in the washing operation.
Gold Mine Wet pan mill applys in the gold mining industry and is one of the indispensable equipment in the modern gold mining industry. In addition, it can also apply for mining and processing other non-ferrous metals and precious metal ore…
Shaking tables for gold recovery, mineral processing at great prices. Learn more about our gold shaking table, prices, and processing today.
loading…
已经是到最后一篇内容了!
We use cookies to ensure that we give you the best experience on our website. If you continue to use this site we will assume that you are happy with it.
Privacy Policy