How to Choose Stone Crusher for Each Crushing Stage
3931Learn correctly select stone crushers for primary, secondary, tertiary stages. Understand jaw, cone, impact, and VSI crushers for optimal aggregate production.
View detailsSearch the whole station Crushing Equipment
The manganese mining landscape in 2026 faces a distinct challenge: the depletion of high-grade oxide reserves. The industry focus has shifted entirely to Refractory Manganese Ore Processing. These deposits are geologically complex, often containing high levels of phosphorus, iron, and silica, or appearing as fine-grained carbonates. Profitability in this sector no longer depends on extraction volume but on beneficiation efficiency. Implementing precise physical and chemical separation circuits is the only viable method to upgrade these difficult ores into marketable concentrates. This technical overview outlines the most effective equipment and flow strategies for modern manganese plants.
Understanding your raw material is the first step. I categorize manganese ores into three main industrial groups based on their mineral composition and processing difficulty.



These are the most common commercial ores. They include minerals like Pyrolusite and Psilomelane. They usually have a high density. Separation is relatively easy using physical methods.
These include Rhodochrosite. They are often finer-grained. The density difference between the ore and the waste rock is small. This makes gravity separation difficult. Flotation or strong magnetic separation is often required.
This is the hardest category. It includes Ferromanganese ores (high iron) or ores with high phosphorus content. Simple physical separation is often not enough. We may need to use roasting or chemical leaching to separate the impurities.

Steel Industry:
90% of global manganese production goes into steelmaking. It is an essential desulfurizing agent. It removes oxygen and sulfur from molten iron. It also converts brittle iron into hard steel. There is no substitute for manganese in this sector.
Battery Sector:
In 2026, the demand from the Electric Vehicle (EV) market is exploding. High-purity manganese sulphate is a key component in lithium-ion batteries. This sector requires the highest grade of processed concentrate.
General Flow:
Every efficient plant follows a four-stage logic: Crushing, Scrubbing, Separation, and Dewatering. I will break down the standard flow we use at ZONEDING for most clients.



Process Details:
First, we reduce the size. But we must be careful not to over-crush. Manganese is brittle. If you crush it to powder too early, you lose it. Next, we wash it. Clay is the enemy of separation. Finally, we separate the valuable mineral from the waste.
| Stage | Equipment | Purpose | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| Crushing | Jaw Crusher | Size Reduction | Dissociate mineral from rock |
| Washing | Sand Washing Machine | Desliming | Remove sticky clay/mud |
| Screening | Vibrating Screen | Classification | Separate by size fractions |
| Beneficiation | Jigs/Magnetic Separators | Separation | Final Concentrate |
Overview:
There is no “one size fits all” machine. I choose the method based on the density, magnetism, and surface chemistry of your specific ore. Here are the four technologies we use.
This is the most cost-effective method. It uses the density difference between manganese (SG 4.0+) and silica (SG 2.6).
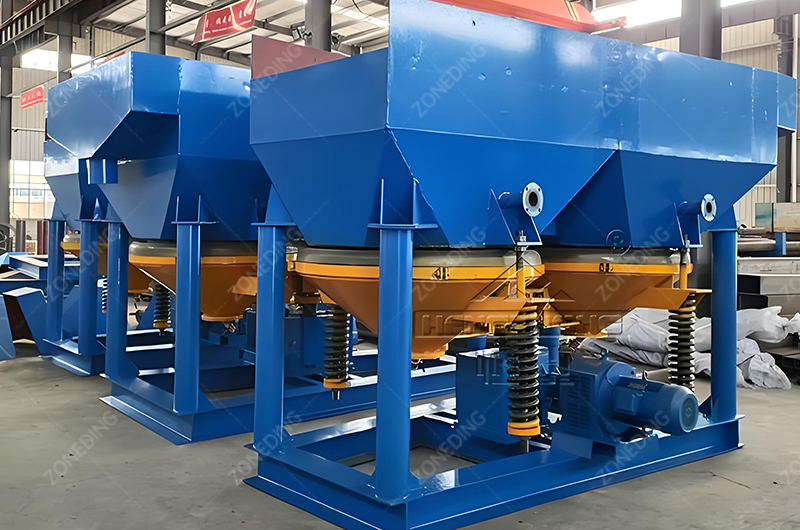


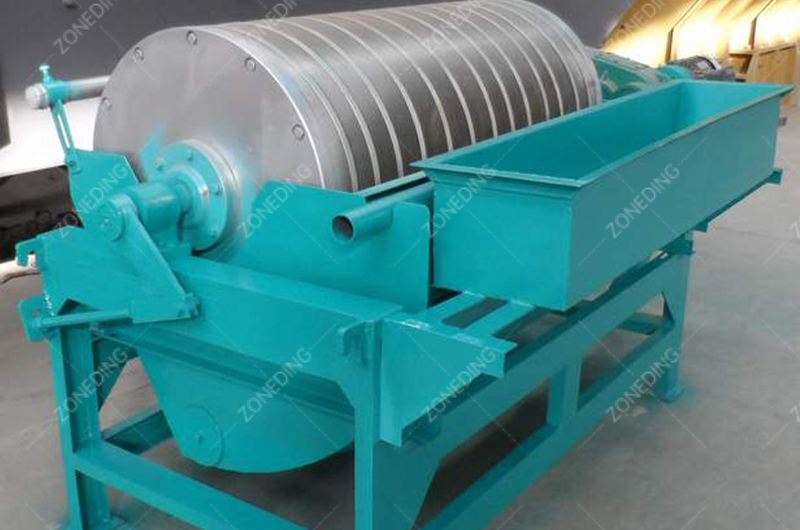
Manganese is weakly magnetic. Iron is strongly magnetic. Silica is non-magnetic.
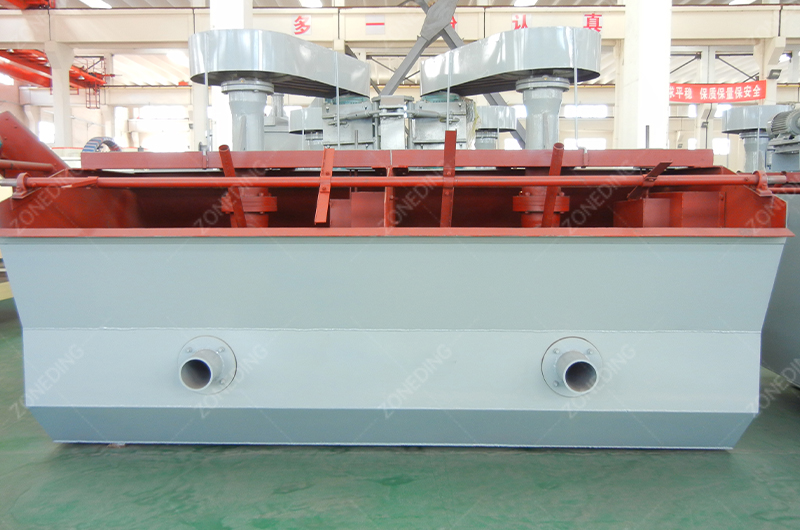

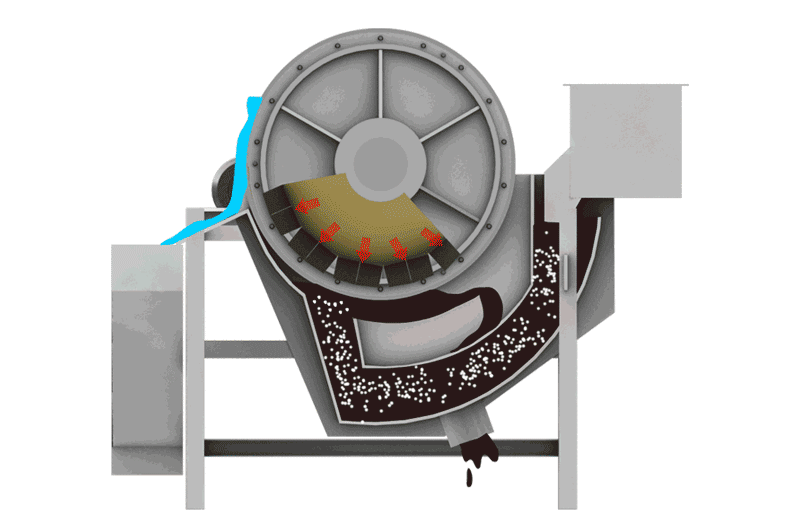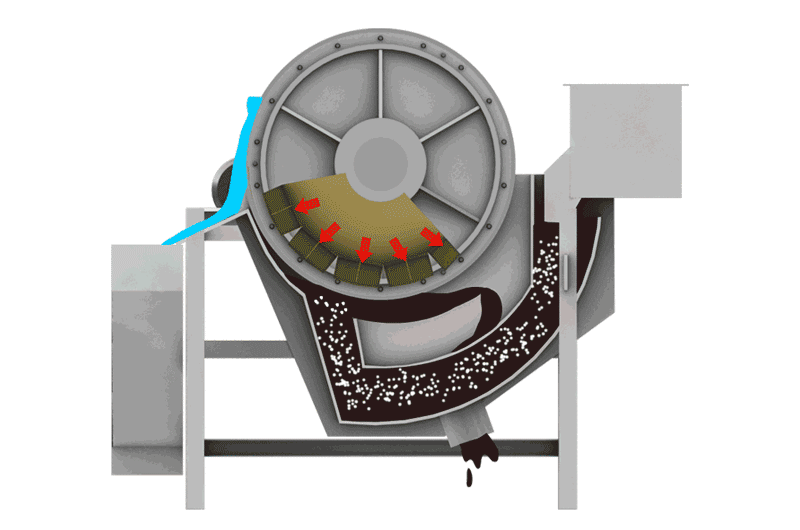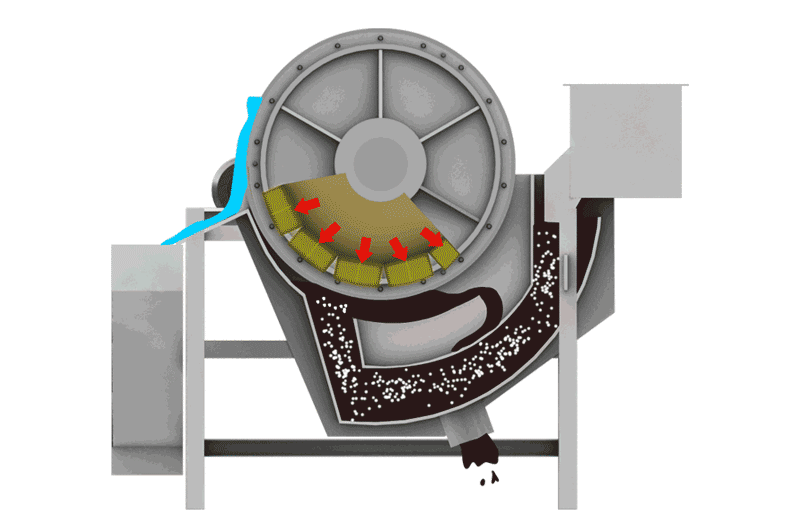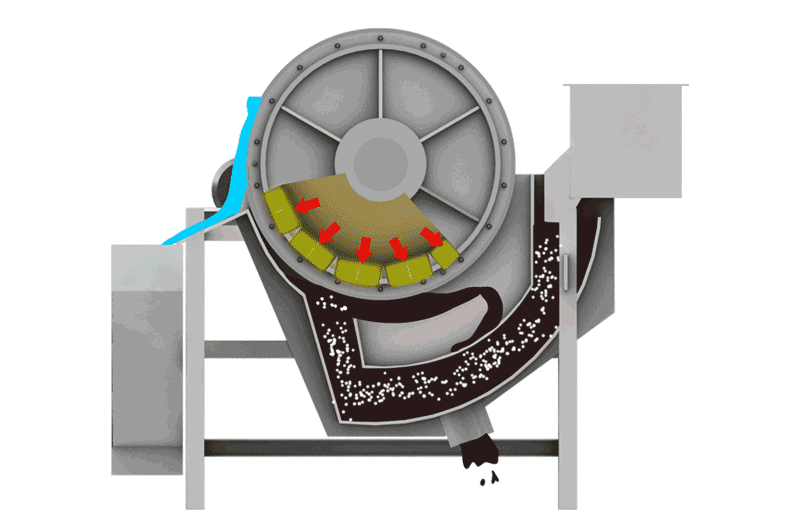


We use this for Manganese Carbonate ores and very fine slimes (-0.074mm). Flotation Machines use chemicals to make manganese bubbles float to the top. It is complex but effective for difficult ores.
Do not skip this. We use a Drum Washer or Log Washer to remove clay. If clay enters the magnetic separator, it blocks the matrix. If it enters flotation, it consumes expensive chemicals.
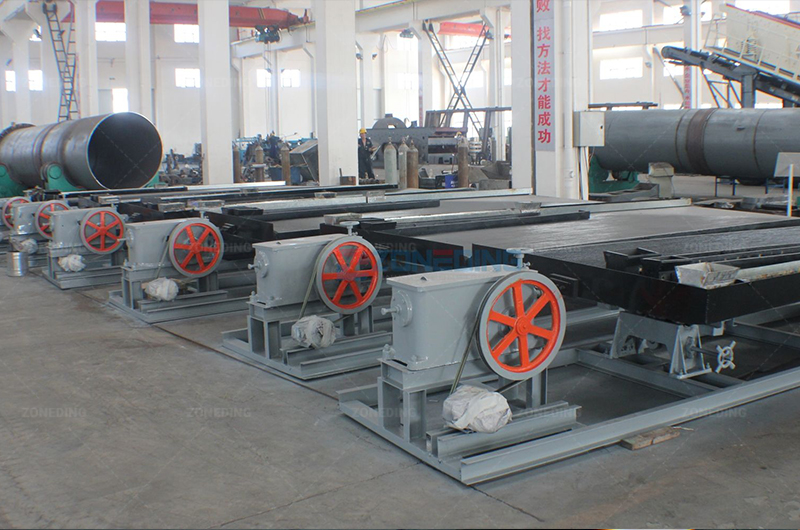
We send the cleaned coarse fraction (6mm-30mm) to the Jig.
The “middlings” (mixed rock) from the Jig and the fines (-6mm) go to a Ball Mill. We grind them to liberate the minerals. Then, we pass them through a High-Gradient Magnetic Separator.
The non-magnetic tailings and ultra-fine slimes go to flotation.
Question 1: How can high-iron manganese ore be separated effectively?
Physical separation is often ineffective due to similar densities. The most reliable method is Manganese Ore Magnetic Roasting using a Rotary Kiln. This process converts iron minerals into magnetic magnetite, allowing separation via low-intensity magnetic separators.
Question 2: Why do high-gradient magnetic separators block frequently?
Blockages occur when fine manganese slimes clog standard steel wool matrices. To prevent this, it is recommended to use a High Gradient Magnetic Separator equipped with a Rod Matrix. The larger gaps and high-frequency pulsation allow slimes to pass while capturing magnetic particles.
Question 3: Is it possible to remove phosphorus using flotation?
Removing phosphorus via flotation is difficult if the phosphorus is chemically bonded or extremely fine. In such cases, physical separation results in high manganese loss. Chemical Leaching Process is the only industrial method to effectively separate phosphorus from manganese in high-phosphorus ores.
Question 4: How does temperature affect manganese carbonate flotation?
Manganese carbonate flotation typically uses fatty acid collectors, which solidify and disperse poorly in cold water. Operating at low temperatures reduces recovery rates. Heating the flotation pulp to above 20°C or using specialized low-temperature reagents is necessary for efficient flotation.
Question 5: What is the best method for processing low-grade manganese ore?
For low-grade ores (<15%), direct grinding is uneconomical. The best approach is pre-concentration using XRT Intelligent Sorting. This technology rejects 40-50% of waste rock at the coarse crushing stage, increasing the feed grade for downstream processing.
ZONEDING Machine is a globally recognized manufacturer of mineral processing equipment, specializing in difficult-to-process ores. From robust Crushing Plants to precision magnetic separation systems, ZONEDING delivers engineered solutions to the mining sector. With a manufacturing base of 8,000 square meters and a dedicated engineering team, the company supports projects in over 120 countries.
Contact ZONEDING engineering for customized flow sheet design and beneficiation testing.
Learn correctly select stone crushers for primary, secondary, tertiary stages. Understand jaw, cone, impact, and VSI crushers for optimal aggregate production.
View detailsOur complete guide walks you through the process of iron removal from kaolin clay. Boost whiteness and quality for industrial applications like ceramics.
View detailsLearn exactly how silver mining works with our step-by-step guide. We break down the complete process, from ore exploration and mining to final refining.
View detailsThe selection between Direct Flotation and Reverse Flotation constitutes a fundamental engineering decision in the design of mineral processing circuits. This choice is not merely based on mineral hydrophobicity but involves a complex analysis of...
View detailsWe use cookies to ensure that we give you the best experience on our website. If you continue to use this site we will assume that you are happy with it.
Privacy Policy