Spiral Classifier vs. Hydrocyclone: Which Is Better?
3893Optimize mineral processing! Compare spiral classifiers vs. hydrocyclones. Learn 5 differences to select ideal equipment for efficiency & beneficiation.
View detailsSearch the whole station Crushing Equipment
Handling sulfidic gold ore is one of the most challenging tasks in mineral processing. It requires high technical skill. The mining machinery industry has seen fifty years of experience. Gold ore beneficiation technology has evolved. It started from simple heap leaching. Now it is a complex, environmentally friendly, multi-stage system. Sulfide gold ores are difficult. Gold particles are often very small. They are inside sulfide minerals. Examples are pyrite, arsenopyrite, and pyrrhotite. Gold can also be closely mixed with them. This means traditional gravity separation or single cyanidation methods often fail. They cannot recover the gold well. A different approach is necessary.
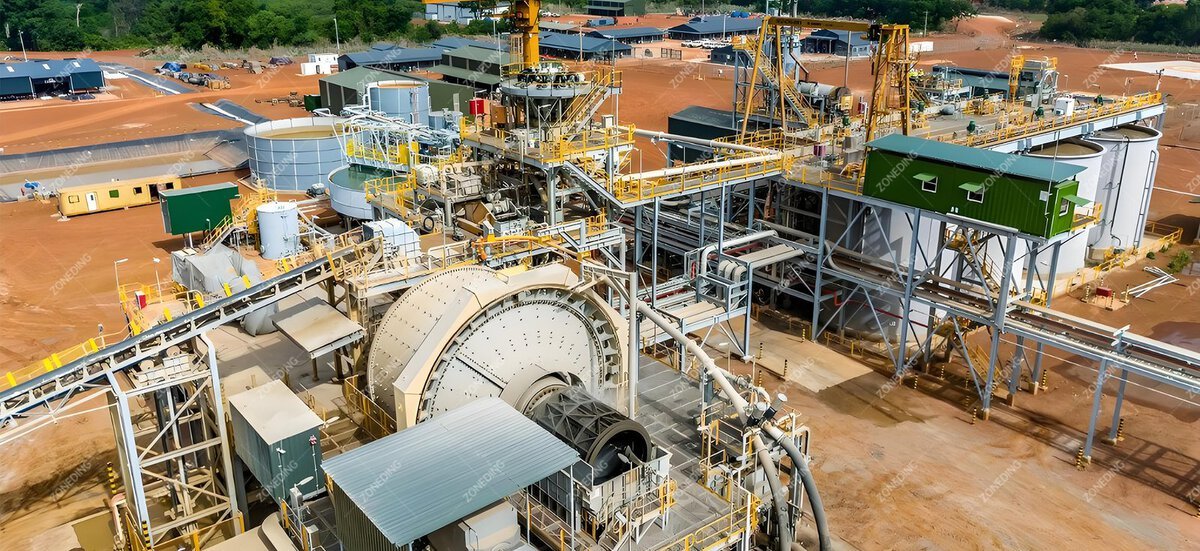

First, the sulfides that hide the gold are treated. Then the gold is extracted. This is not just about choosing equipment. It is a system engineering project. It needs deep thought. A balance must be found. This includes ore characteristics, processing methods, environmental rules, and profit. No single step is enough. All aspects must be considered. Here are seven important points. Stemming from decades of experience in separating sulfidic gold ore, these insights are often overlooked.
Many people just look at the gold grade report. However, for refractory sulfide gold ore, the gold grade is only part of the story. The true deciding factor is how the gold exists. Is it free gold, in cracks, or wrapped inside sulfides or silicates? How big are the gold particles?
Selecting a processing method without full mineral analysis is a big risk. Analysis like SEM-MLA, QEMSCAN, and microprobe helps. It shows gold’s size, what minerals it is with, how much, and how exposed the gold is. A gold particle of a few micrometers inside pyrite is different. A free 100-micrometer gold particle is also different. Their recovery methods will be very different.
Such analysis directly tells what grinding size is needed. It helps choose the method. It also shows if pre-oxidation is needed. This detailed understanding of is the first step. It is key to effective and profitable gold recovery.



Gold in refractory sulfide gold ore is often “locked.” This means it is hidden inside other minerals. These minerals are usually sulfides like pyrite, arsenopyrite, or pyrrhotite. The gold particles are usually very small. They can be less than a micron. Because they are hidden, common methods cannot reach them. This is why the ore is called “refractory.”
Traditional recovery methods fail here. Gravity separation cannot separate gold from the host mineral. Direct cyanidation cannot dissolve the gold. The cyanide solution cannot touch the gold. So, special steps are needed. The gold needs to be exposed first. This exposure happens through pre-treatment. Then methods like cyanidation can be used. This process is complex. It needs a good understanding of the ore. This ensures high gold extraction rate.
Many people think flotation just floats all sulfides. However, the real skill in sulfide gold ore flotation is precise separation.
For complex sulfide gold ore, multi-stage flotation is commonly employed. It might even involve floating in different phases:
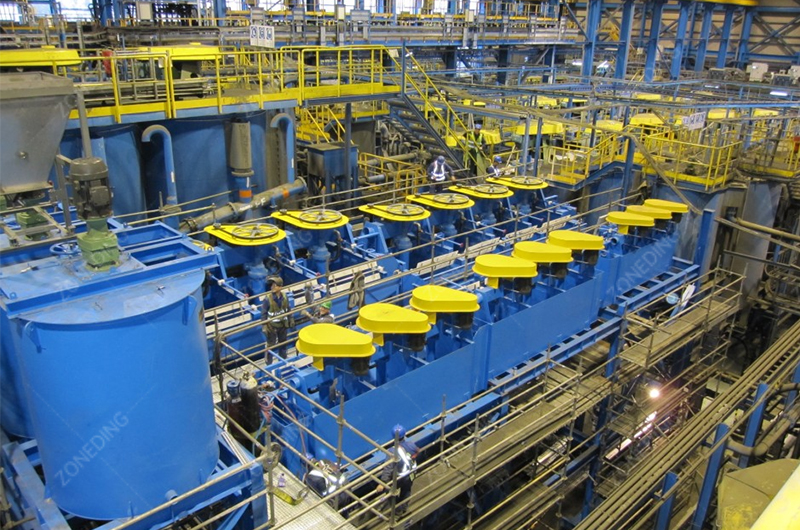


The selection and dosage of flotation reagents are critical. Collectors attach to the sulfide particles. They make them hydrophobic. Frothers create a stable foam. Adjusters control the process. They help separate different minerals. For example, lime might be used to suppress pyrite. This allows other sulfides to float first.
The flotation circuit design is also important. It includes roughing, scavenging, and cleaning stages. Roughing recovers most of the valuable minerals quickly. Scavenging recovers any remaining minerals. Cleaning refines the concentrate. It increases its grade. This multi-stage approach ensures high gold recovery into a high-grade gold concentrate. This concentrate is then ready for pre-treatment. ZONEDING provides a range of flotation machine types to suit various ore characteristics. They ensure optimal recovery.
When gold is wrapped in sulfides, the sulfide crystals must be broken down. This exposes the gold. This is done through oxidation. Common pre-oxidation methods include roasting, pressure oxidation (POX), and biological oxidation (BIOX). Choosing a method is challenging for many operators.
There is no single “best” pre-oxidation method. Only the one “most suitable” for a specific ore. This depends on budget, environmental rules, and operating ability. Deep testing in labs and pilot plants is a must. This decides success for years to come.
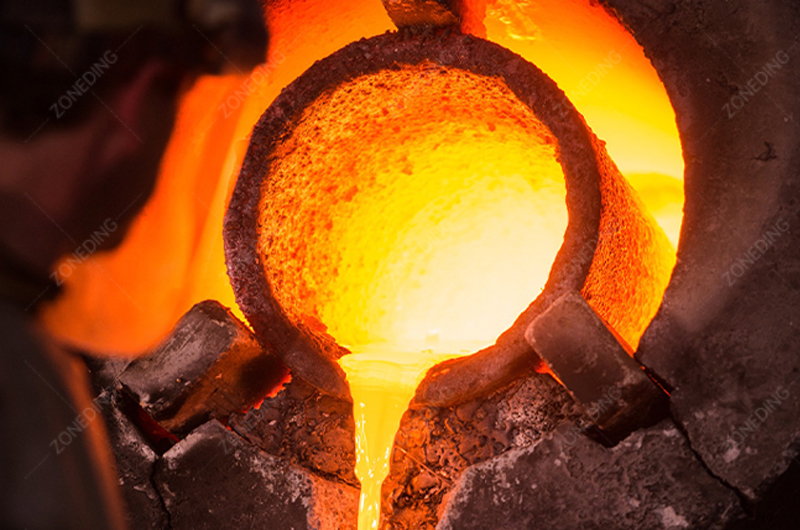

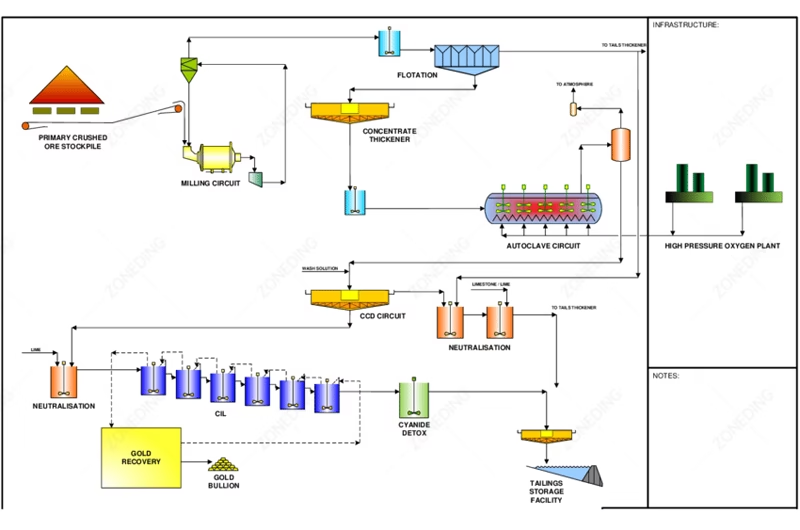
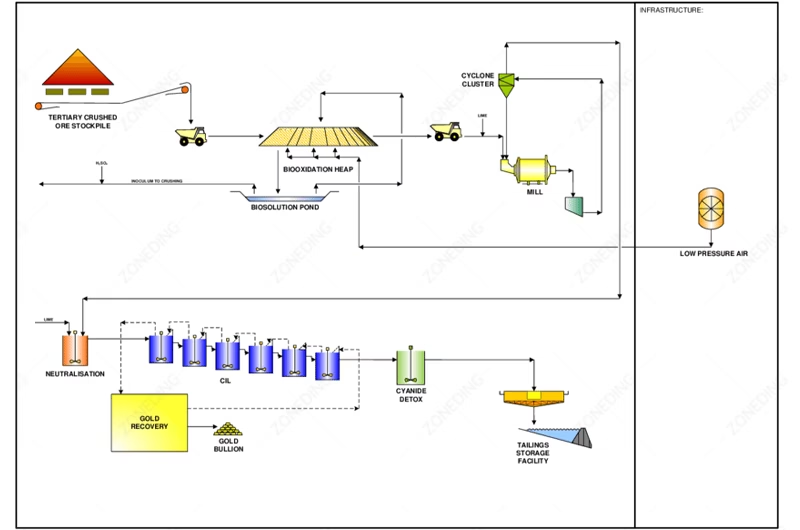
Gold ore roasting is suitable for ores with high arsenic. It also works for ores with dense sulfides where gold is finely enclosed. Roasting burns off the sulfur and arsenic. This creates a porous structure. The gold becomes accessible.
However, it has drawbacks. Controlling SO2 and arsenic dust emissions is hard. Fuel costs are high. Equipment materials must withstand high temperatures. Choosing the right furnace type is key. Controlling temperature is also critical. Over-roasting must be avoided. This can form insoluble phases. Under-roasting means incomplete oxidation. ZONEDING’s rotary kiln and other drying equipment can be adapted for specific roasting applications.
Pressure oxidation (POX) suits high-sulfur ores. It is good for ores with very fine gold. It works well for tightly enclosed gold. POX yields high recovery. But, equipment investment is huge. This includes autoclaves and acid-resistant materials. Operating costs are also high. Oxygen and steam are needed. It requires very skilled operation and maintenance. It is a main method today. It is also quite environmentally friendly.
Bio-oxidation leaching uses microbes to oxidize sulfides. Investment and operating costs are lower. It is also environmentally friendly mineral processing. But, the treatment takes longer. It can be days or even weeks. Temperature, pH, and ore poisons (like antimony, copper) affect it greatly. It is less adaptable to different ores. It usually works for ores with medium to low sulfur and arsenic.
Besides the main methods, new technologies are developing. These include:
After pre-treatment, the gold-rich material is ready for extraction. Gold ore cyanidation leaching is the most common method. It dissolves gold.
Pre-treated materials are different from raw ore. They are more porous. They have a larger surface area. They might have some oxidation byproducts. This makes cyanide solution reach gold better. Gold dissolves faster. But, cyanide consumption might increase. This happens if oxidation is not complete. Leftover sulfides consume cyanide. Also, soluble metal salts (like iron salts) can form. This affects carbon adsorption.
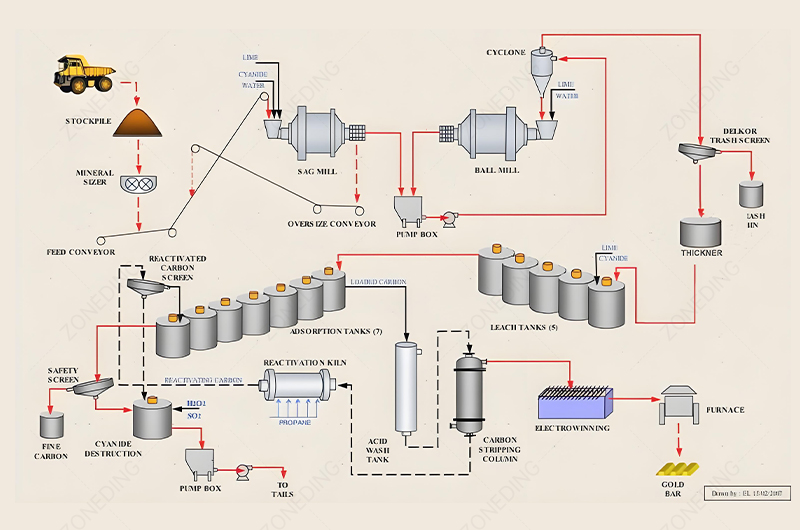
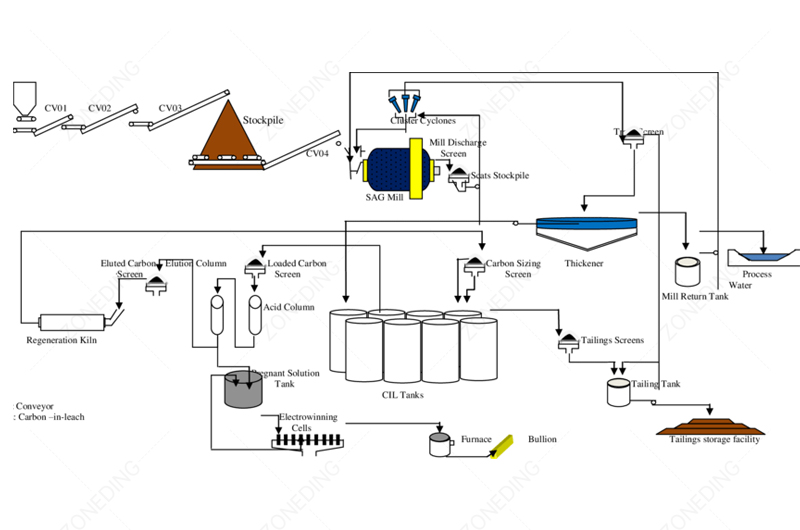
The CIL/CIP process is still standard. But, special attention must be paid to:
Safety is paramount in cyanidation. Strict controls are needed for handling and storing cyanide. Monitoring systems detect leaks. Emergency response plans are in place. This protects workers and the environment.
Efficiency means maximizing gold recovery. It also means minimizing cyanide use. Good agitation in the tanks ensures proper contact. Optimal pH levels maintain cyanide stability. Carbon management is key. This includes regular carbon regeneration. These steps make the gold recovery process both safe and effective.
Complex sulfide gold ore often contains other valuable or harmful metals. These can be copper, lead, zinc, antimony, silver, or rare metals. In the past, only gold was focused on. But now, all valuable elements must be considered. Harmful ones also require management. This is important in today’s resource market.
If the ore has a lot of copper, the copper concentrate should be floated first. If it has antimony, a special process is needed. This separates or fixes antimony. It improves gold concentrate grade. It also lowers environmental risk.
Working with multiple metals helps in two ways. It creates more income. It also turns harmful elements into useful resources. This lowers waste treatment costs. It boosts the project’s overall profit and environmental benefits. This needs smart design. Full elemental analysis during ore testing is crucial.
An integrated flowsheet combines different technologies. This might include:
Choosing the best gold extraction plan is vital. It must fit the ore. It must be economical. It must follow environmental rules. This is a complex task.
First, ore characteristics must be known. What is the gold’s occurrence? What are the sulfide minerals? What are the associated harmful elements? This detailed knowledge is the base for choosing pre-treatment. It helps decide the gold recovery process.
Next, economics must be considered. This includes upfront investment. It covers operating costs. These are chemicals, energy, and labor. Each process has different costs. Roasting has high fuel costs. POX has high equipment costs. BIOX has longer processing times. These factors need to be balanced. High gold recovery with good profit is desired. This balance is key. It makes the gold processing plant viable.
Finally, environmental regulations are very important. Local laws dictate emissions. They control waste disposal. Methods like roasting have air pollution risks. Cyanidation has waste water risks. A compliant process must be chosen. It should also be sustainable. This includes water recycling and tailings management. Investing in environmentally friendly mineral processing often pays off. It avoids fines. It builds a good public image. ZONEDING assists in navigating these choices. The company designs a plan that meets all client needs.
Question 1: Why is sulfide gold ore processing considered refractory?
Refractory sulfide gold ore is difficult because gold is locked inside sulfide minerals. Traditional methods cannot easily reach and dissolve the gold. This needs special pre-treatment to expose the gold.
Question 2: What is the main purpose of gold concentrate pre-treatment?
Gold concentrate pre-treatment aims to break down the sulfide minerals that encapsulate gold. This exposes the gold particles. It makes them accessible for subsequent leaching, boosting gold recovery.
Question 3: Is gold ore roasting an environmentally friendly option?
Gold ore roasting can release SO2 and arsenic dust. This poses environmental challenges. However, modern roasting plants use advanced gas cleaning systems. They mitigate these emissions significantly.
Question 4: What are the key advantages of bio-oxidation leaching?
Bio-oxidation leaching has lower energy and operating costs. It is environmentally friendly. It uses microbes to oxidize sulfides. This avoids high temperatures and pressures.
Question 5: How does ZONEDING help with gold extraction plan selection?
ZONEDING provides expert consultation. The company analyzes ore characteristics. It considers economic goals. It evaluates environmental regulations. Then it designs a customized, optimal gold extraction plan.
Processing sulfidic gold ore is a complex journey. It needs a deep understanding of gold’s occurrence. It requires advanced pre-treatment technologies. These include flotation, roasting, POX, and BIOX. Each step aims to liberate gold. Then, efficient cyanide leaching recovers the gold. Integrated approaches are often necessary. They maximize both economic and environmental benefits. The ore, economics, and environmental rules must be considered. This ensures the best gold extraction plan.
ZONEDING recommends thorough ore analysis. It suggests detailed feasibility studies. This ensures the chosen process is tailored. It must be efficient and profitable. Partnering with ZONEDING assists in navigating these complexities. This ensures successful sulfide gold ore processing.
ZONEDING MACHINE is a leading Chinese mineral processing equipment manufacturer. It specializes in B2B solutions. ZONEDING has provided reliable equipment since 2004. The factory covers 8,000 square meters. It produces over 500 units annually. The product range is comprehensive. It covers crushing, grinding, beneficiation, screening, and drying. ZONEDING offers full-service support. This includes design, manufacturing, installation, training, and after-sales service. Products export to over 120 countries. ZONEDING commits to delivering high-quality, customized, and efficient solutions. These help operations achieve their goals.
Contact ZONEDING today to discuss sulfidic gold ore processing needs.
Optimize mineral processing! Compare spiral classifiers vs. hydrocyclones. Learn 5 differences to select ideal equipment for efficiency & beneficiation.
View detailsMaking the right choice is critical. We break down the 4 main cone crusher types and guide you through key selection factors like feed size and capacity.
View detailsLearn the full dolomite processing line, from primary crushing with a jaw crusher to fine grinding with a Raymond mill. Select the right equipment for your plant.
View detailsGain critical insights into hydraulic cone crushers. Understand principle and key features to make informed decisions for aggregate or mining applications.
View details